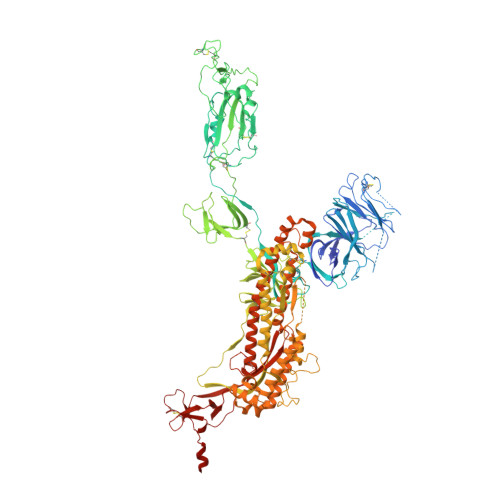
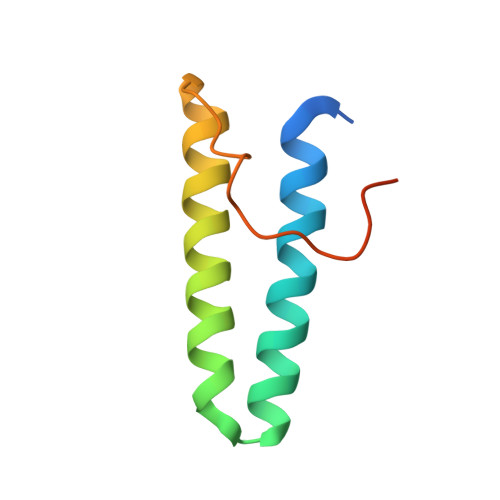
De novo design of protein interactions with learned surface fingerprints.
Gainza, P., Wehrle, S., Van Hall-Beauvais, A., Marchand, A., Scheck, A., Harteveld, Z., Buckley, S., Ni, D., Tan, S., Sverrisson, F., Goverde, C., Turelli, P., Raclot, C., Teslenko, A., Pacesa, M., Rosset, S., Georgeon, S., Marsden, J., Petruzzella, A., Liu, K., Xu, Z., Chai, Y., Han, P., Gao, G.F., Oricchio, E., Fierz, B., Trono, D., Stahlberg, H., Bronstein, M., Correia, B.E.(2023) Nature 617: 176-184
- PubMed: 37100904
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-023-05993-x
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7XAD, 7XYQ, 7ZRV, 7ZSD, 7ZSS - PubMed Abstract:
Physical interactions between proteins are essential for most biological processes governing life 1 . However, the molecular determinants of such interactions have been challenging to understand, even as genomic, proteomic and structural data increase. This knowledge gap has been a major obstacle for the comprehensive understanding of cellular protein-protein interaction networks and for the de novo design of protein binders that are crucial for synthetic biology and translational applications 2-9 . Here we use a geometric deep-learning framework operating on protein surfaces that generates fingerprints to describe geometric and chemical features that are critical to drive protein-protein interactions 10 . We hypothesized that these fingerprints capture the key aspects of molecular recognition that represent a new paradigm in the computational design of novel protein interactions. As a proof of principle, we computationally designed several de novo protein binders to engage four protein targets: SARS-CoV-2 spike, PD-1, PD-L1 and CTLA-4. Several designs were experimentally optimized, whereas others were generated purely in silico, reaching nanomolar affinity with structural and mutational characterization showing highly accurate predictions. Overall, our surface-centric approach captures the physical and chemical determinants of molecular recognition, enabling an approach for the de novo design of protein interactions and, more broadly, of artificial proteins with function.
- Laboratory of Protein Design and Immunoengineering, Institute of Bioengineering, École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne, Lausanne, Switzerland.
Organizational Affiliation: