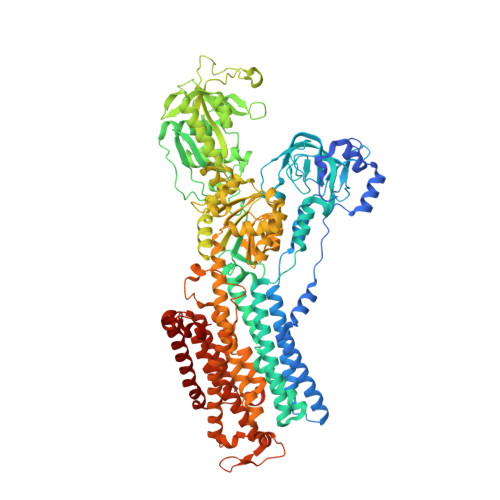
Specific protonation of acidic residues confers K + selectivity to the gastric proton pump.
Madapally, H.V., Abe, K., Dubey, V., Khandelia, H.(2023) J Biological Chem 300: 105542-105542
- PubMed: 38072058
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbc.2023.105542
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8WA5 - PubMed Abstract:
The gastric proton pump (H + ,K + -ATPase) transports a proton into the stomach lumen for every K + ion exchanged in the opposite direction. In the lumen-facing state of the pump (E2), the pump selectively binds K + despite the presence of a 10-fold higher concentration of Na + . The molecular basis for the ion selectivity of the pump is unknown. Using molecular dynamics simulations, free energy calculations, and Na + and K + -dependent ATPase activity assays, we demonstrate that the K + selectivity of the pump depends upon the simultaneous protonation of the acidic residues E343 and E795 in the ion-binding site. We also show that when E936 is protonated, the pump becomes Na + sensitive. The protonation-mimetic mutant E936Q exhibits weak Na + -activated ATPase activity. A 2.5-Å resolution cryo-EM structure of the E936Q mutant in the K + -occluded E2-Pi form shows, however, no significant structural difference compared with wildtype except less-than-ideal coordination of K + in the mutant. The selectivity toward a specific ion correlates with a more rigid and less fluctuating ion-binding site. Despite being exposed to a pH of 1, the fundamental principle driving the K + ion selectivity of H + ,K + -ATPase is similar to that of Na + ,K + -ATPase: the ionization states of the acidic residues in the ion-binding sites determine ion selectivity. Unlike the Na + ,K + -ATPase, however, protonation of an ion-binding glutamate residue (E936) confers Na + sensitivity.
- PHYLIFE, Physical Life Science, Department of Physics Chemistry and Pharmacy, University of Southern Denmark, Odense, Denmark.
Organizational Affiliation: