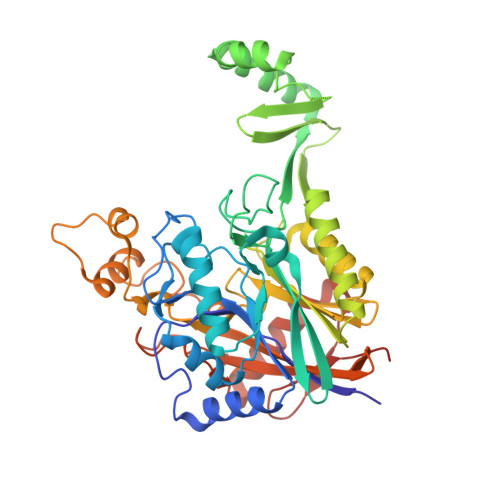
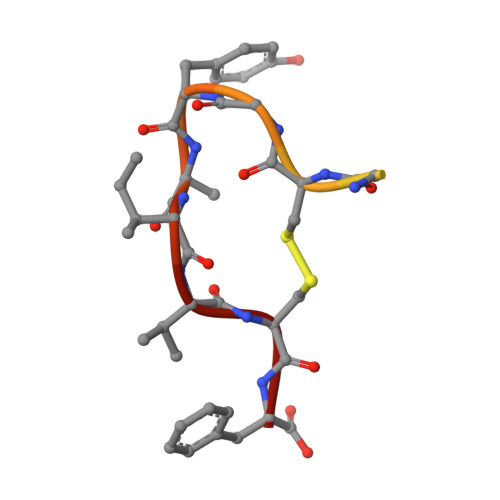
Structure of lasso peptide epimerase MslH reveals metal-dependent acid/base catalytic mechanism.
Nakashima, Y., Kawakami, A., Ogasawara, Y., Maeki, M., Tokeshi, M., Dairi, T., Morita, H.(2023) Nat Commun 14: 4752-4752
- PubMed: 37550286
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-023-40232-x
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8GQ9, 8GQA, 8GQB, 8ITG, 8ITH - PubMed Abstract:
The lasso peptide MS-271 is a ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptide (RiPP) consisting of 21 amino acids with D-tryptophan at the C-terminus, and is derived from the precursor peptide MslA. MslH, encoded in the MS-271 biosynthetic gene cluster (msl), catalyzes the epimerization at the Cα center of the MslA C-terminal Trp21, leading to epi-MslA. The detailed catalytic process, including the catalytic site and cofactors, has remained enigmatic. Herein, based on X-ray crystallographic studies in association with MslA core peptide analogues, we show that MslH is a metallo-dependent peptide epimerase with a calcineurin-like fold. The crystal structure analysis, followed by site-directed mutagenesis, docking simulation, and ICP-MS studies demonstrate that MslH employs acid/base chemistry to facilitate the reversible epimerization of the C-terminal Trp21 of MslA, by utilizing two pairs of His/Asp catalytic residues that are electrostatically tethered to a six-coordination motif with a Ca(II) ion via water molecules.
- Institute of Natural Medicine, University of Toyama, 2630-Sugitani, Toyama, 930-0194, Japan.
Organizational Affiliation: