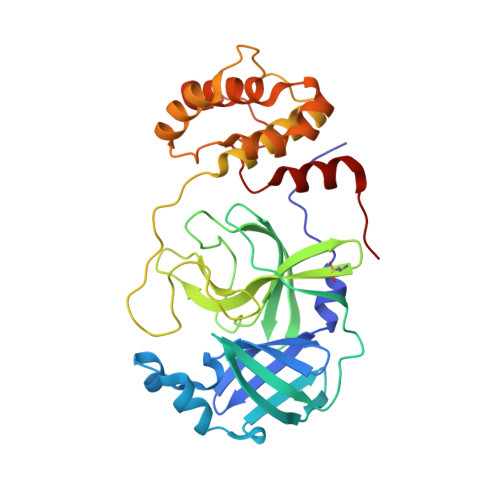
In vitro selection of macrocyclic peptide inhibitors containing cyclic gamma 2,4 -amino acids targeting the SARS-CoV-2 main protease.
Miura, T., Malla, T.R., Owen, C.D., Tumber, A., Brewitz, L., McDonough, M.A., Salah, E., Terasaka, N., Katoh, T., Lukacik, P., Strain-Damerell, C., Mikolajek, H., Walsh, M.A., Kawamura, A., Schofield, C.J., Suga, H.(2023) Nat Chem 15: 998-1005
- PubMed: 37217786
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41557-023-01205-1
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7Z4S - PubMed Abstract:
γ-Amino acids can play important roles in the biological activities of natural products; however, the ribosomal incorporation of γ-amino acids into peptides is challenging. Here we report how a selection campaign employing a non-canonical peptide library containing cyclic γ 2,4 -amino acids resulted in the discovery of very potent inhibitors of the SARS-CoV-2 main protease (M pro ). Two kinds of cyclic γ 2,4 -amino acids, cis-3-aminocyclobutane carboxylic acid (γ 1 ) and (1R,3S)-3-aminocyclopentane carboxylic acid (γ 2 ), were ribosomally introduced into a library of thioether-macrocyclic peptides. One resultant potent M pro inhibitor (half-maximal inhibitory concentration = 50 nM), GM4, comprising 13 residues with γ 1 at the fourth position, manifests a 5.2 nM dissociation constant. An M pro :GM4 complex crystal structure reveals the intact inhibitor spans the substrate binding cleft. The γ 1 interacts with the S1' catalytic subsite and contributes to a 12-fold increase in proteolytic stability compared to its alanine-substituted variant. Knowledge of interactions between GM4 and M pro enabled production of a variant with a 5-fold increase in potency.
- Department of Chemistry, Graduate School of Science, The University of Tokyo, Tokyo, Japan.
Organizational Affiliation: