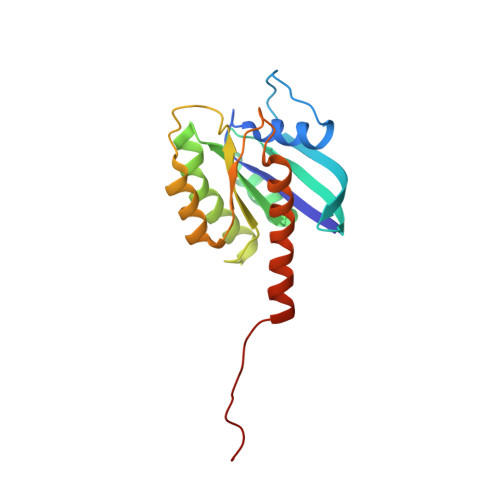
Oncogenic KRAS G12D mutation promotes dimerization through a second, phosphatidylserine-dependent interface: a model for KRAS oligomerization.
Lee, K.Y., Enomoto, M., Gebregiworgis, T., Gasmi-Seabrook, G.M.C., Ikura, M., Marshall, C.B.(2021) Chem Sci 12: 12827-12837
- PubMed: 34703570
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1039/d1sc03484g
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7RSC, 7RSE - PubMed Abstract:
KRAS forms transient dimers and higher-order multimers (nanoclusters) on the plasma membrane, which drive MAPK signaling and cell proliferation. KRAS is a frequently mutated oncogene, and while it is well known that the most prevalent mutation, G12D, impairs GTP hydrolysis, thereby increasing KRAS activation, G12D has also been shown to enhance nanoclustering. Elucidating structures of dynamic KRAS assemblies on a membrane has been challenging, thus we have refined our NMR approach that uses nanodiscs to study KRAS associated with membranes. We incorporated paramagnetic relaxation enhancement (PRE) titrations and interface mutagenesis, which revealed that, in addition to the symmetric 'α-α' dimerization interface shared with wild-type KRAS, the G12D mutant also self-associates through an asymmetric 'α-β' interface. The 'α-β' association is dependent on the presence of phosphatidylserine lipids, consistent with previous reports that this lipid promotes KRAS self-assembly on the plasma membrane in cells. Experiments using engineered mutants to spoil each interface, together with PRE probes attached to the membrane or free in solvent, suggest that dimerization through the primary 'α-α' interface releases β interfaces from the membrane promoting formation of the secondary 'α-β' interaction, potentially initiating nanoclustering. In addition, the small molecule BI-2852 binds at a β-β interface, stabilizing a new dimer configuration that outcompetes native dimerization and blocks the effector-binding site. Our data indicate that KRAS self-association involves a delicately balanced conformational equilibrium between transient states, which is sensitive to disease-associated mutation and small molecule inhibitors. The methods developed here are applicable to biologically important transient interactions involving other membrane-associated proteins.
- Princess Margaret Cancer Centre, University Health Network Toronto Ontario M5G 1L7 Canada mitsu.ikura@uhnresearch.ca chris.marshall@uhnresearch.ca.
Organizational Affiliation: