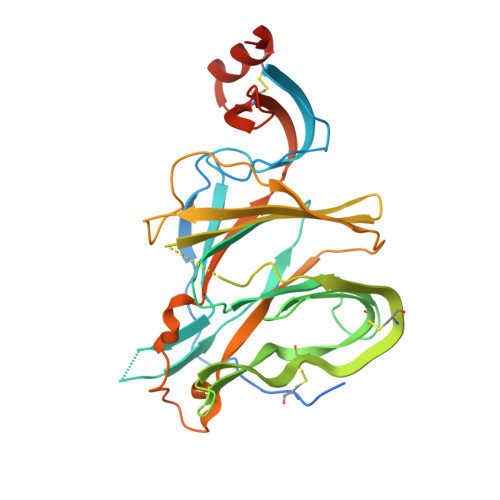
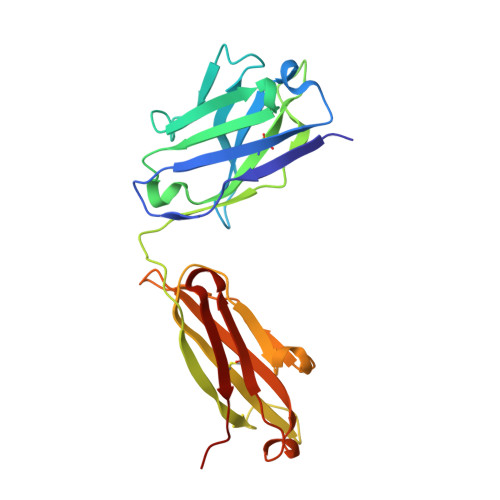
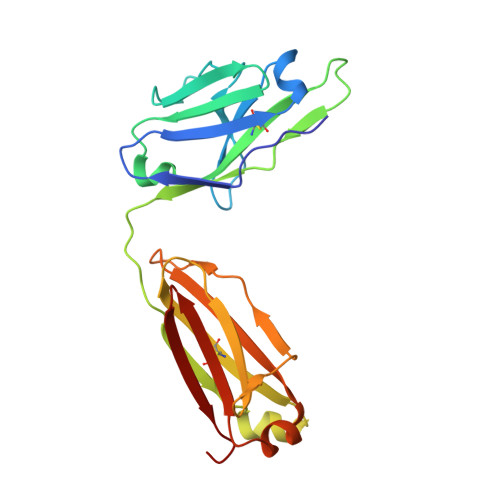
N-terminal domain antigenic mapping reveals a site of vulnerability for SARS-CoV-2.
McCallum, M., De Marco, A., Lempp, F.A., Tortorici, M.A., Pinto, D., Walls, A.C., Beltramello, M., Chen, A., Liu, Z., Zatta, F., Zepeda, S., di Iulio, J., Bowen, J.E., Montiel-Ruiz, M., Zhou, J., Rosen, L.E., Bianchi, S., Guarino, B., Fregni, C.S., Abdelnabi, R., Foo, S.C., Rothlauf, P.W., Bloyet, L.M., Benigni, F., Cameroni, E., Neyts, J., Riva, A., Snell, G., Telenti, A., Whelan, S.P.J., Virgin, H.W., Corti, D., Pizzuto, M.S., Veesler, D.(2021) Cell 184: 2332
- PubMed: 33761326
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2021.03.028
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7LXW, 7LXX, 7LXY, 7LXZ, 7LY0, 7LY2, 7LY3 - PubMed Abstract:
The SARS-CoV-2 spike (S) glycoprotein contains an immunodominant receptor-binding domain (RBD) targeted by most neutralizing antibodies (Abs) in COVID-19 patient plasma. Little is known about neutralizing Abs binding to epitopes outside the RBD and their contribution to protection. Here, we describe 41 human monoclonal Abs (mAbs) derived from memory B cells, which recognize the SARS-CoV-2 S N-terminal domain (NTD) and show that a subset of them neutralize SARS-CoV-2 ultrapotently. We define an antigenic map of the SARS-CoV-2 NTD and identify a supersite (designated site i) recognized by all known NTD-specific neutralizing mAbs. These mAbs inhibit cell-to-cell fusion, activate effector functions, and protect Syrian hamsters from SARS-CoV-2 challenge, albeit selecting escape mutants in some animals. Indeed, several SARS-CoV-2 variants, including the B.1.1.7, B.1.351, and P.1 lineages, harbor frequent mutations within the NTD supersite, suggesting ongoing selective pressure and the importance of NTD-specific neutralizing mAbs for protective immunity and vaccine design.
- Department of Biochemistry, University of Washington, Seattle, WA 98195, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: