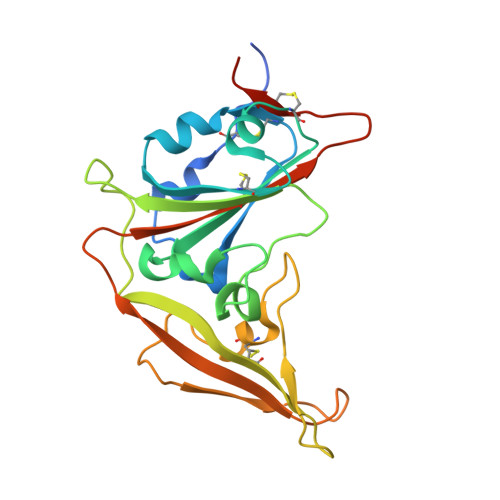
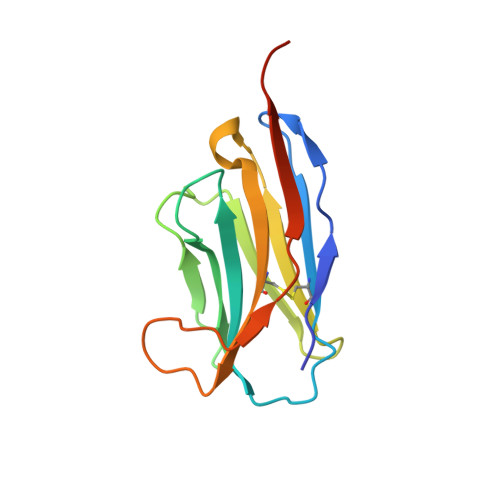
Structural Basis for Potent Neutralization of Betacoronaviruses by Single-Domain Camelid Antibodies.
Wrapp, D., De Vlieger, D., Corbett, K.S., Torres, G.M., Wang, N., Van Breedam, W., Roose, K., van Schie, L., Hoffmann, M., Pohlmann, S., Graham, B.S., Callewaert, N., Schepens, B., Saelens, X., McLellan, J.S.(2020) Cell 181: 1004
- PubMed: 32375025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2020.04.031
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6WAQ, 6WAR - PubMed Abstract:
Coronaviruses make use of a large envelope protein called spike (S) to engage host cell receptors and catalyze membrane fusion. Because of the vital role that these S proteins play, they represent a vulnerable target for the development of therapeutics. Here, we describe the isolation of single-domain antibodies (VHHs) from a llama immunized with prefusion-stabilized coronavirus spikes. These VHHs neutralize MERS-CoV or SARS-CoV-1 S pseudotyped viruses, respectively. Crystal structures of these VHHs bound to their respective viral targets reveal two distinct epitopes, but both VHHs interfere with receptor binding. We also show cross-reactivity between the SARS-CoV-1 S-directed VHH and SARS-CoV-2 S and demonstrate that this cross-reactive VHH neutralizes SARS-CoV-2 S pseudotyped viruses as a bivalent human IgG Fc-fusion. These data provide a molecular basis for the neutralization of pathogenic betacoronaviruses by VHHs and suggest that these molecules may serve as useful therapeutics during coronavirus outbreaks.
- Department of Molecular Biosciences, The University of Texas at Austin, Austin, TX 78712, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: