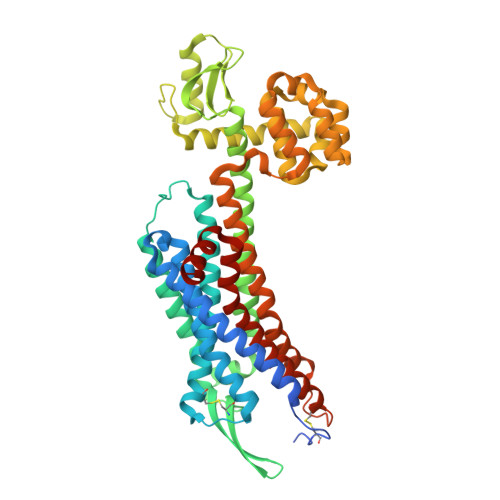
Crystal structures of human ETBreceptor provide mechanistic insight into receptor activation and partial activation.
Shihoya, W., Izume, T., Inoue, A., Yamashita, K., Kadji, F.M.N., Hirata, K., Aoki, J., Nishizawa, T., Nureki, O.(2018) Nat Commun 9: 4711-4711
- PubMed: 30413709
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-07094-0
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6IGK, 6IGL - PubMed Abstract:
Endothelin receptors (ET A and ET B ) are class A GPCRs activated by vasoactive peptide endothelins, and are involved in blood pressure regulation. ET B -selective signalling induces vasorelaxation, and thus selective ET B agonists are expected to be utilized for improved anti-tumour drug delivery and neuroprotection. Here, we report the crystal structures of human ET B receptor in complex with ET B -selective agonist, endothelin-3 and an ET B -selective endothelin analogue IRL1620. The structure of the endothelin-3-bound receptor reveals that the disruption of water-mediated interactions between W6.48 and D2.50 is critical for receptor activation, while these hydrogen-bonding interactions are partially preserved in the IRL1620-bound structure. Consistently, functional analysis reveals the partial agonistic effect of IRL1620. The current findings clarify the detailed molecular mechanism for the coupling between the orthosteric pocket and the G-protein binding, and the partial agonistic effect of IRL1620, thus paving the way for the design of improved agonistic drugs targeting ET B .
- Department of Biological Sciences, Graduate School of Science, The University of Tokyo, Bunkyo, Tokyo, 113-0033, Japan.
Organizational Affiliation: