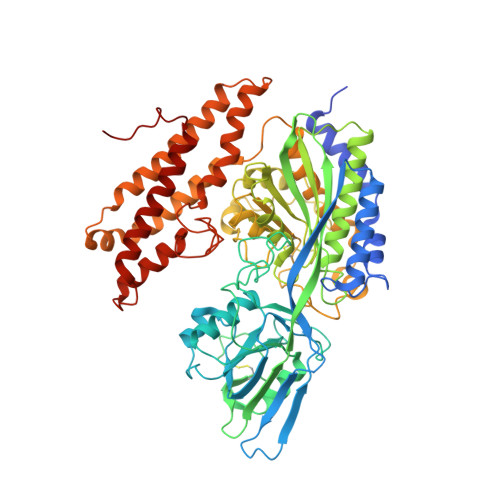
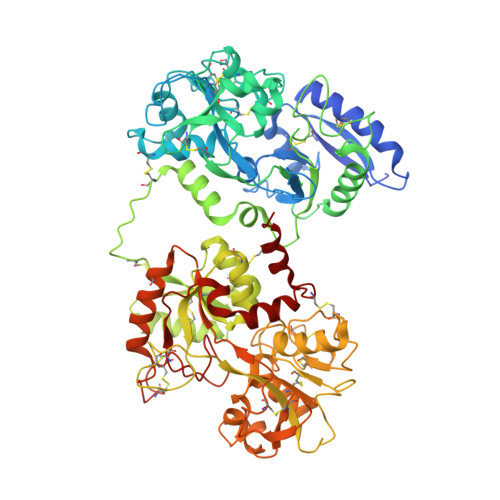
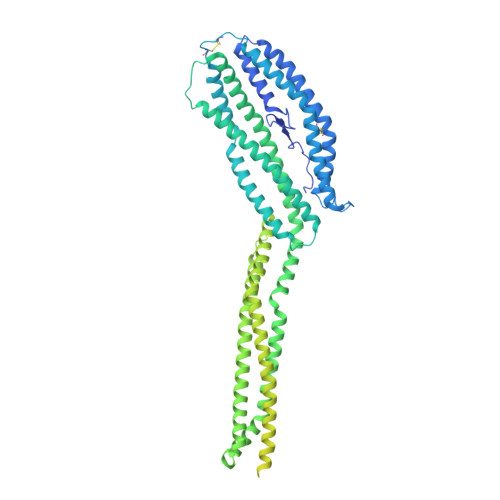
Cryo-EM structure of an essential Plasmodium vivax invasion complex.
Gruszczyk, J., Huang, R.K., Chan, L.J., Menant, S., Hong, C., Murphy, J.M., Mok, Y.F., Griffin, M.D.W., Pearson, R.D., Wong, W., Cowman, A.F., Yu, Z., Tham, W.H.(2018) Nature 559: 135-139
- PubMed: 29950717
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-018-0249-1
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6BPA, 6BPB, 6BPC, 6BPD, 6BPE, 6D03, 6D04, 6D05 - PubMed Abstract:
Plasmodium vivax is the most widely distributed malaria parasite that infects humans 1 . P. vivax invades reticulocytes exclusively, and successful entry depends on specific interactions between the P. vivax reticulocyte-binding protein 2b (PvRBP2b) and transferrin receptor 1 (TfR1) 2 . TfR1-deficient erythroid cells are refractory to invasion by P. vivax, and anti-PvRBP2b monoclonal antibodies inhibit reticulocyte binding and block P. vivax invasion in field isolates 2 . Here we report a high-resolution cryo-electron microscopy structure of a ternary complex of PvRBP2b bound to human TfR1 and transferrin, at 3.7 Å resolution. Mutational analyses show that PvRBP2b residues involved in complex formation are conserved; this suggests that antigens could be designed that act across P. vivax strains. Functional analyses of TfR1 highlight how P. vivax hijacks TfR1, an essential housekeeping protein, by binding to sites that govern host specificity, without affecting its cellular function of transporting iron. Crystal and solution structures of PvRBP2b in complex with antibody fragments characterize the inhibitory epitopes. Our results establish a structural framework for understanding how P. vivax reticulocyte-binding protein engages its receptor and the molecular mechanism of inhibitory monoclonal antibodies, providing important information for the design of novel vaccine candidates.
- The Walter and Eliza Hall Institute of Medical Research, Parkville, Victoria, Australia.
Organizational Affiliation: