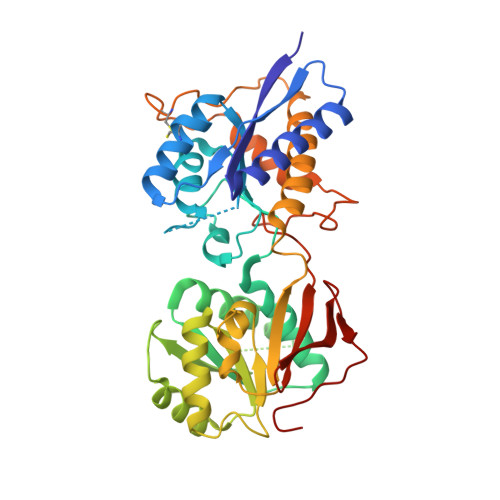
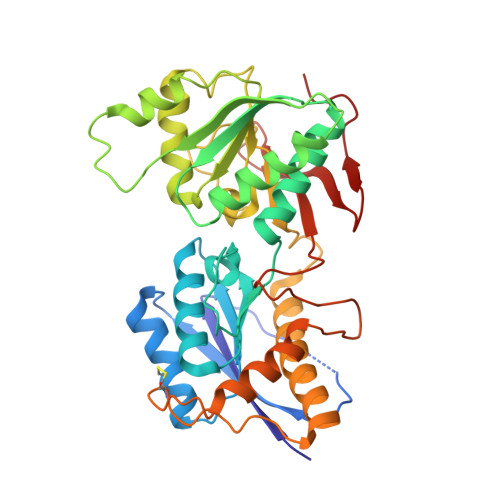
Molecular Basis for Subtype Specificity and High-Affinity Zinc Inhibition in the GluN1-GluN2A NMDA Receptor Amino-Terminal Domain.
Romero-Hernandez, A., Simorowski, N., Karakas, E., Furukawa, H.(2016) Neuron 92: 1324-1336
- PubMed: 27916457
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2016.11.006
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5TPW, 5TPZ, 5TQ0, 5TQ2 - PubMed Abstract:
Zinc is vastly present in the mammalian brain and controls functions of various cell surface receptors to regulate neurotransmission. A distinctive characteristic of N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptors containing a GluN2A subunit is that their ion channel activity is allosterically inhibited by a nano-molar concentration of zinc that binds to an extracellular domain called an amino-terminal domain (ATD). Despite physiological importance, the molecular mechanism underlying the high-affinity zinc inhibition has been incomplete because of the lack of a GluN2A ATD structure. Here we show the first crystal structures of the heterodimeric GluN1-GluN2A ATD, which provide the complete map of the high-affinity zinc-binding site and reveal distinctive features from the ATD of the GluN1-GluN2B subtype. Perturbation of hydrogen bond networks at the hinge of the GluN2A bi-lobe structure affects both zinc inhibition and open probability, supporting the general model in which the bi-lobe motion in ATD regulates the channel activity in NMDA receptors.
- WM Keck Structural Biology Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, NY 11724, USA; Watson School of Biological Sciences, Cold Spring Harbor, NY 11724, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: