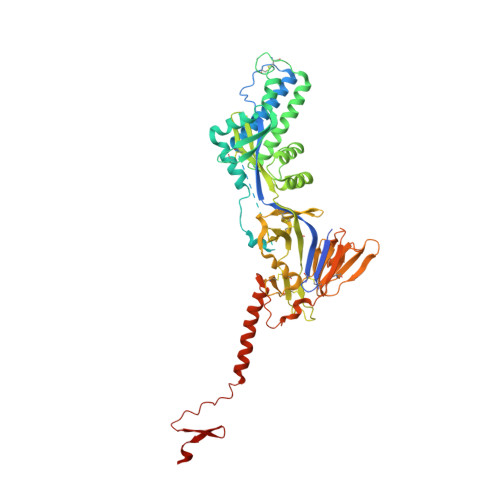
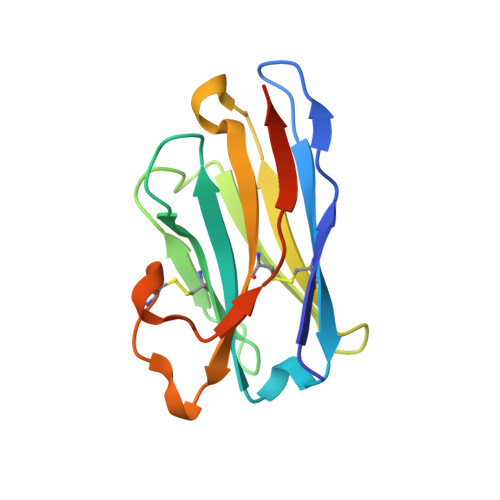
Potent single-domain antibodies that arrest respiratory syncytial virus fusion protein in its prefusion state.
Rossey, I., Gilman, M.S., Kabeche, S.C., Sedeyn, K., Wrapp, D., Kanekiyo, M., Chen, M., Mas, V., Spitaels, J., Melero, J.A., Graham, B.S., Schepens, B., McLellan, J.S., Saelens, X.(2017) Nat Commun 8: 14158-14158
- PubMed: 28194013
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms14158
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
5TOJ, 5TOK, 5TP3 - PubMed Abstract:
Human respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) is the main cause of lower respiratory tract infections in young children. The RSV fusion protein (F) is highly conserved and is the only viral membrane protein that is essential for infection. The prefusion conformation of RSV F is considered the most relevant target for antiviral strategies because it is the fusion-competent form of the protein and the primary target of neutralizing activity present in human serum. Here, we describe two llama-derived single-domain antibodies (VHHs) that have potent RSV-neutralizing activity and bind selectively to prefusion RSV F with picomolar affinity. Crystal structures of these VHHs in complex with prefusion F show that they recognize a conserved cavity formed by two F protomers. In addition, the VHHs prevent RSV replication and lung infiltration of inflammatory monocytes and T cells in RSV-challenged mice. These prefusion F-specific VHHs represent promising antiviral agents against RSV.
- Medical Biotechnology Center, VIB, Technologiepark 927, Ghent B-9052, Belgium.
Organizational Affiliation: