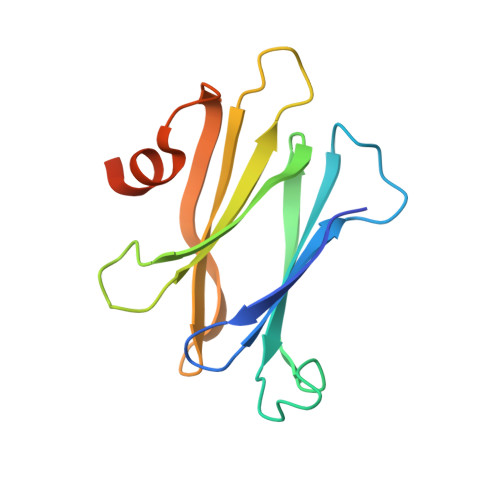
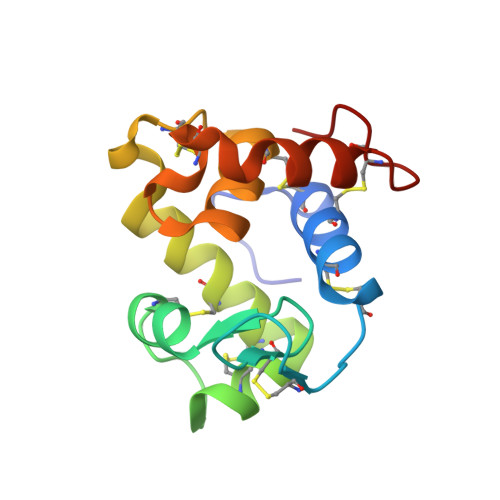
The structure of the proteinaceous inhibitor PliI from Aeromonas hydrophila in complex with its target lysozyme.
Leysen, S., Van Herreweghe, J.M., Yoneda, K., Ogata, M., Usui, T., Araki, T., Michiels, C.W., Strelkov, S.V.(2015) Acta Crystallogr D Biol Crystallogr 71: 344-351
- PubMed: 25664745
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1107/S1399004714025863
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4PJ2 - PubMed Abstract:
Recent microbiological data have revealed that Gram-negative bacteria are able to protect themselves against the lytic action of host lysozymes by secreting proteinaceous inhibitors. Four distinct classes of such inhibitors have been discovered that specifically act against c-type, g-type and i-type lysozymes. Here, the 1.24 Å resolution crystal structure of the periplasmic i-type lysozyme inhibitor from Aeromonas hydrophila (PliI-Ah) in complex with the i-type lysozyme from Meretrix lusoria is reported. The structure is the first to explain the inhibitory mechanism of the PliI family at the atomic level. A distinct `ridge' formed by three exposed PliI loops inserts into the substrate-binding groove of the lysozyme, resulting in a complementary `key-lock' interface. The interface is principally stabilized by the interactions made by the PliI-Ah residues Ser104 and Tyr107 belonging to the conserved SGxY motif, as well as by the other conserved residues Ser46 and Asp76. The functional importance of these residues is confirmed by inhibition assays with the corresponding point mutants of PliI-Ah. The accumulated structural data on lysozyme-inhibitor complexes from several classes indicate that in all cases an extensive interface of either a single or a double `key-lock' type is formed, resulting in highly efficient inhibition. These data provide a basis for the rational development of a new class of antibacterial drugs.
- Laboratory for Biocrystallography, Department of Pharmaceutical and Pharmacological Sciences, KU Leuven, 3000 Leuven, Belgium.
Organizational Affiliation: