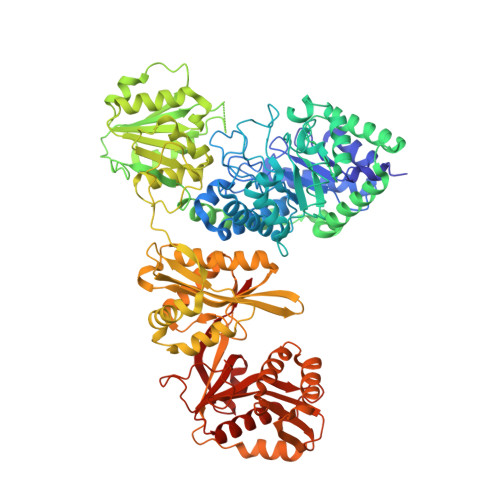
A unique GCN5-related glucosamine N-acetyltransferase region exist in the fungal multi-domain glycoside hydrolase family 3 beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase
Qin, Z., Xiao, Y., Yang, X., Mesters, J.R., Yang, S., Jiang, Z.(2015) Sci Rep 5: 18292-18292
- PubMed: 26669854
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/srep18292
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4ZM6 - PubMed Abstract:
Glycoside hydrolase (GH) family 3 β-N-acetylglucosaminidases widely exist in the filamentous fungi, which may play a key role in chitin metabolism of fungi. A multi-domain GH family 3 β-N-acetylglucosaminidase from Rhizomucor miehei (RmNag), exhibiting a potential N-acetyltransferase region, has been recently reported to show great potential in industrial applications. In this study, the crystal structure of RmNag was determined at 2.80 Å resolution. The three-dimensional structure of RmNag showed four distinctive domains, which belong to two distinguishable functional regions--a GH family 3 β-N-acetylglucosaminidase region (N-terminal) and a N-acetyltransferase region (C-terminal). From structural and functional analysis, the C-terminal region of RmNag was identified as a unique tandem array linking general control non-derepressible 5 (GCN5)-related N-acetyltransferase (GNAT), which displayed glucosamine N-acetyltransferase activity. Structural analysis of this glucosamine N-acetyltransferase region revealed that a unique glucosamine binding pocket is located in the pantetheine arm binding terminal region of the conserved CoA binding pocket, which is different from all known GNAT members. This is the first structural report of a glucosamine N-acetyltransferase, which provides novel structural information about substrate specificity of GNATs. The structural and functional features of this multi-domain β-N-acetylglucosaminidase could be useful in studying the catalytic mechanism of GH family 3 proteins.
- College of Food Science and Nutritional Engineering, Beijing Advanced Innovation Center for Food Nutrition and Human Health, China Agricultural University, Beijing 100083, China.
Organizational Affiliation: