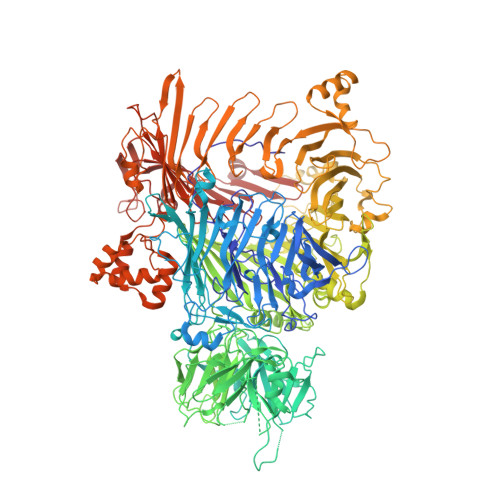
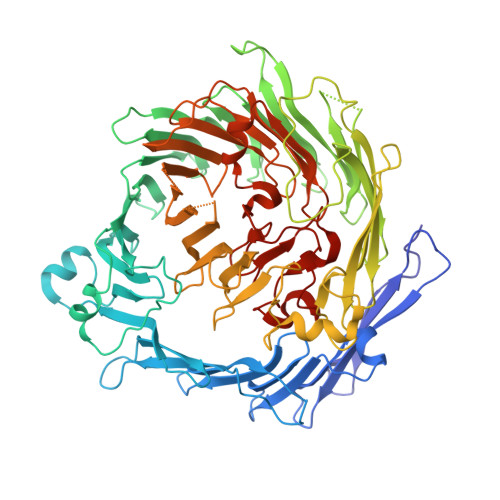
The BC component of ABC toxins is an RHS-repeat-containing protein encapsulation device
Busby, J.N., Panjikar, S., Landsberg, M.J., Hurst, M.R.H., Lott, J.S.(2013) Nature 501: 547-550
- PubMed: 23913273
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nature12465
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
4DWS, 4IGL - PubMed Abstract:
The ABC toxin complexes produced by certain bacteria are of interest owing to their potent insecticidal activity and potential role in human disease. These complexes comprise at least three proteins (A, B and C), which must assemble to be fully toxic. The carboxy-terminal region of the C protein is the main cytotoxic component, and is poorly conserved between different toxin complexes. A general model of action has been proposed, in which the toxin complex binds to the cell surface via the A protein, is endocytosed, and subsequently forms a pH-triggered channel, allowing the translocation of C into the cytoplasm, where it can cause cytoskeletal disruption in both insect and mammalian cells. Toxin complexes have been visualized using single-particle electron microscopy, but no high-resolution structures of the components are available, and the role of the B protein in the mechanism of toxicity remains unknown. Here we report the three-dimensional structure of the complex formed between the B and C proteins, determined to 2.5 Å by X-ray crystallography. These proteins assemble to form an unprecedented, large hollow structure that encapsulates and sequesters the cytotoxic, C-terminal region of the C protein like the shell of an egg. The shell is decorated on one end by a β-propeller domain, which mediates attachment of the B-C heterodimer to the A protein in the native complex. The structure reveals how C auto-proteolyses when folded in complex with B. The C protein is the first example, to our knowledge, of a structure that contains rearrangement hotspot (RHS) repeats, and illustrates a marked structural architecture that is probably conserved across both this widely distributed bacterial protein family and the related eukaryotic tyrosine-aspartate (YD)-repeat-containing protein family, which includes the teneurins. The structure provides the first clues about the function of these protein repeat families, and suggests a generic mechanism for protein encapsulation and delivery.
- AgResearch Structural Biology Laboratory, School of Biological Sciences, The University of Auckland, Auckland 1142, New Zealand.
Organizational Affiliation: