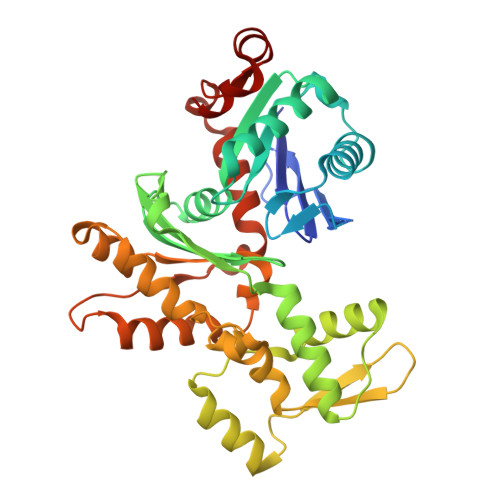
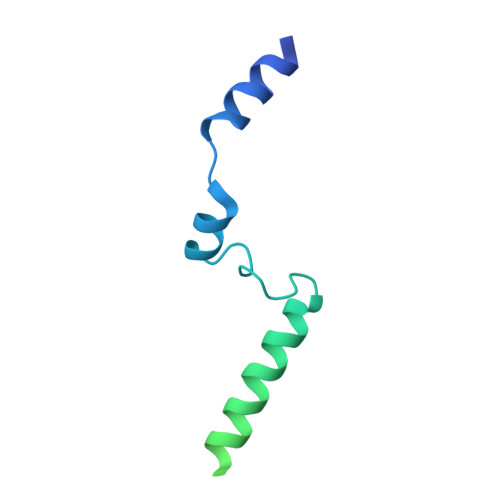
Structure of a pentavalent G-actin*MRTF-A complex reveals how G-actin controls nucleocytoplasmic shuttling of a transcriptional coactivator.
Mouilleron, S., Langer, C.A., Guettler, S., McDonald, N.Q., Treisman, R.(2011) Sci Signal 4: ra40-ra40
- PubMed: 21673315
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1126/scisignal.2001750
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2YJE, 2YJF - PubMed Abstract:
Subcellular localization of the actin-binding transcriptional coactivator MRTF-A is controlled by its interaction with monomeric actin (G-actin). Signal-induced decreases in G-actin concentration reduce MRTF-A nuclear export, leading to its nuclear accumulation, whereas artificial increases in G-actin concentration in resting cells block MRTF-A nuclear import, retaining it in the cytoplasm. This regulation is dependent on three actin-binding RPEL motifs in the regulatory domain of MRTF-A. We describe the structures of pentavalent and trivalent G-actin•RPEL domain complexes. In the pentavalent complex, each RPEL motif and the two intervening spacer sequences bound an actin monomer, forming a compact assembly. In contrast, the trivalent complex lacked the C-terminal spacer- and RPEL-actins, both of which bound only weakly in the pentavalent complex. Cytoplasmic localization of MRTF-A in unstimulated fibroblasts also required binding of G-actin to the spacer sequences. The bipartite MRTF-A nuclear localization sequence was buried in the pentameric assembly, explaining how increases in G-actin concentration prevent nuclear import of MRTF-A. Analyses of the pentavalent and trivalent complexes show how actin loads onto the RPEL domain and reveal a molecular mechanism by which actin can control the activity of one of its binding partners.
- Structural Biology Group, Cancer Research UK London Research Institute, Lincoln's Inn Fields Laboratories, 44 Lincoln's Inn Fields, London WC2A 3LY, UK.
Organizational Affiliation: