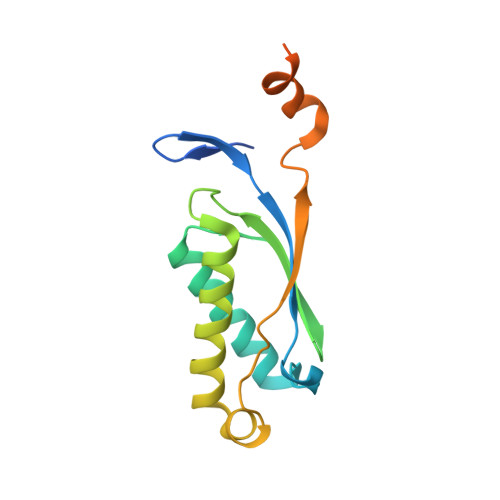
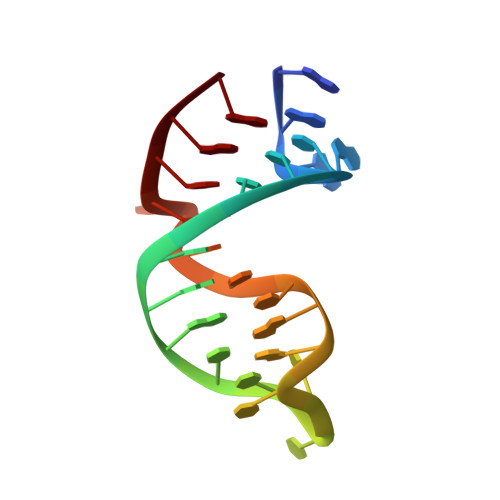
Mechanism of is200/is605 Family DNA Transposases: Activation and Transposon-Directed Target Site Selection.
Barabas, O., Ronning, D.R., Guynet, C., Hickman, A.B., Ton-Hoang, B., Chandler, M., Dyda, F.(2008) Cell 132: 208
- PubMed: 18243097
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2007.12.029
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2VHG, 2VIC, 2VIH, 2VJU, 2VJV - PubMed Abstract:
The smallest known DNA transposases are those from the IS200/IS605 family. Here we show how the interplay of protein and DNA activates TnpA, the Helicobacter pylori IS608 transposase, for catalysis. First, transposon end binding causes a conformational change that aligns catalytically important protein residues within the active site. Subsequent precise cleavage at the left and right ends, the steps that liberate the transposon from its donor site, does not involve a site-specific DNA-binding domain. Rather, cleavage site recognition occurs by complementary base pairing with a TnpA-bound subterminal transposon DNA segment. Thus, the enzyme active site is constructed from elements of both protein and DNA, reminiscent of the interdependence of protein and RNA in the ribosome. Our structural results explain why the transposon ends are asymmetric and how the transposon selects a target site for integration, and they allow us to propose a molecular model for the entire transposition reaction.
- Laboratory of Molecular Biology, National Institute of Diabetes, Digestive, and Kidney Diseases, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD 20892, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: