Structural, dynamic, and chemical characterization of a novel s-glycosylated bacteriocin.
Venugopal, H., Edwards, P.J., Schwalbe, M., Claridge, J.K., Libich, D.S., Stepper, J., Loo, T., Patchett, M.L., Norris, G.E., Pascal, S.M.(2011) Biochemistry 50: 2748-2755
- PubMed: 21395300
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/bi200217u
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
2KUY - PubMed Abstract:
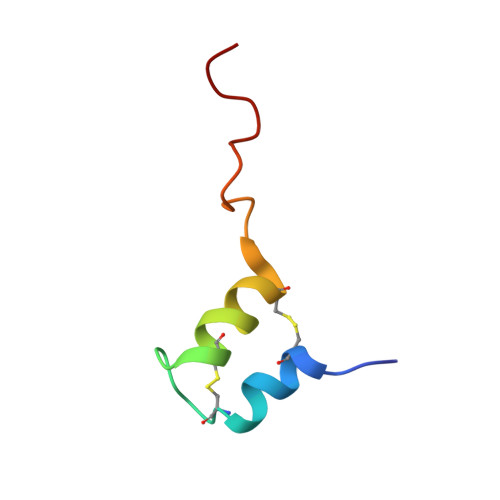
Bacteriocins are bacterial peptides with specific activity against competing species. They hold great potential as natural preservatives and for their probiotic effects. We show here nuclear magnetic resonance-based evidence that glycocin F, a 43-amino acid bacteriocin from Lactobacillus plantarum, contains two β-linked N-acetylglucosamine moieties, attached via side chain linkages to a serine via oxygen, and to a cysteine via sulfur. The latter linkage is novel and has helped to establish a new type of post-translational modification, the S-linked sugar. The peptide conformation consists primarily of two α-helices held together by a pair of nested disulfide bonds. The serine-linked sugar is positioned on a short loop sequentially connecting the two helices, while the cysteine-linked sugar presents at the end of a long disordered C-terminal tail. The differing chemical and conformational stabilities of the two N-actetylglucosamine moieties provide clues about the possible mode of action of this bacteriostatic peptide.
- Institute of Fundamental Sciences, Massey University, Palmerston North, New Zealand. h.venugopal@massey.ac.nz
Organizational Affiliation: