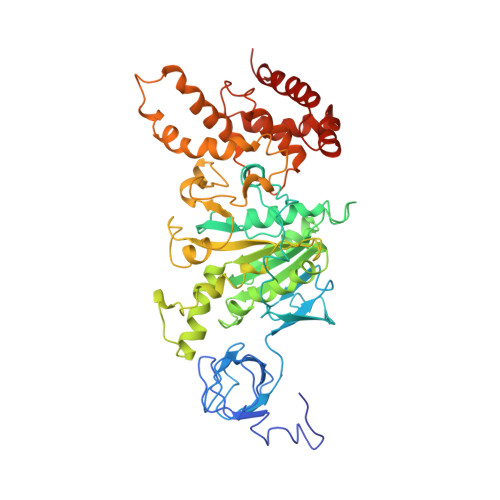
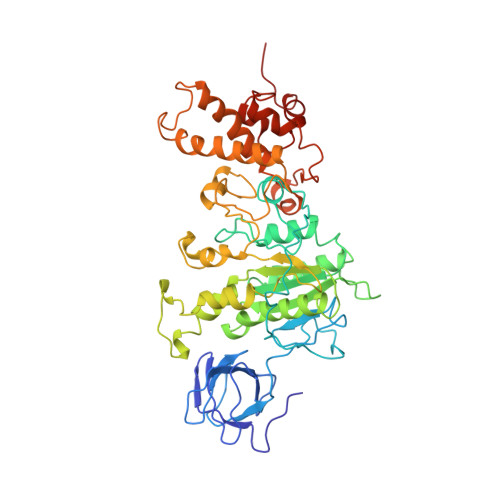
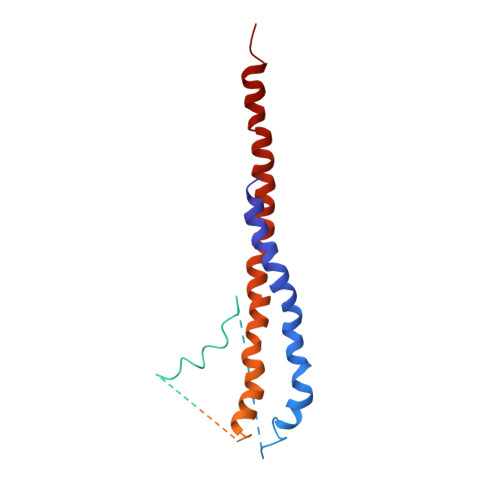
The 2.8-A structure of rat liver F1-ATPase: configuration of a critical intermediate in ATP synthesis/hydrolysis.
Bianchet, M.A., Hullihen, J., Pedersen, P.L., Amzel, L.M.(1998) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95: 11065-11070
- PubMed: 9736690
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.95.19.11065
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
1MAB - PubMed Abstract:
During mitochondrial ATP synthesis, F1-ATPase-the portion of the ATP synthase that contains the catalytic and regulatory nucleotide binding sites-undergoes a series of concerted conformational changes that couple proton translocation to the synthesis of the high levels of ATP required for cellular function. In the structure of the rat liver F1-ATPase, determined to 2.8-A resolution in the presence of physiological concentrations of nucleotides, all three beta subunits contain bound nucleotide and adopt similar conformations. This structure provides the missing configuration of F1 necessary to define all intermediates in the reaction pathway. Incorporation of this structure suggests a mechanism of ATP synthesis/hydrolysis in which configurations of the enzyme with three bound nucleotides play an essential role.
- Department of Biophysics and Biophysical Chemistry, The Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, 725 North Wolfe Street, Baltimore, MD 21205-2185, USA. mario@neruda.med.jhmi.edu
Organizational Affiliation: