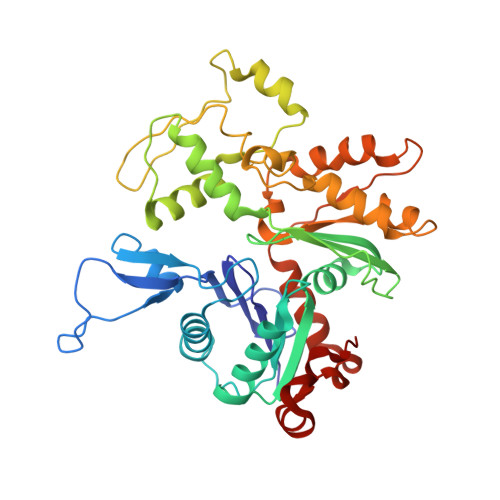
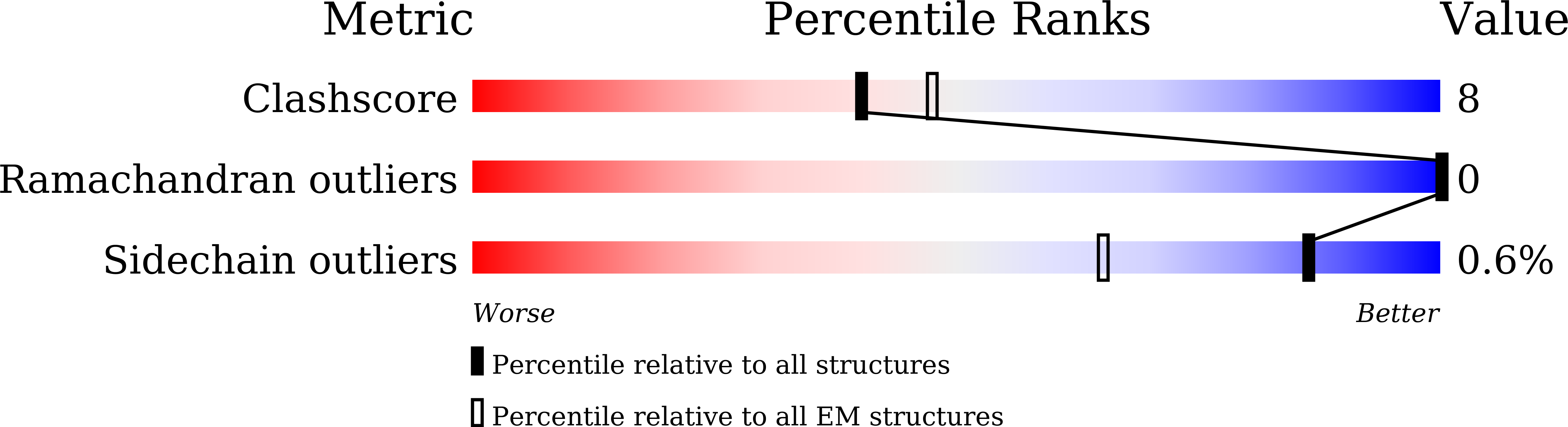Cryo-EM Structure of Actin Filaments fromZea maysPollen.
Ren, Z., Zhang, Y., Zhang, Y., He, Y., Du, P., Wang, Z., Sun, F., Ren, H.(2019) Plant Cell 31: 2855-2867
- PubMed: 31628168
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.18.00973
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6IUG - PubMed Abstract:
Actins are among the most abundant and conserved proteins in eukaryotic cells, where they form filamentous structures that perform vital roles in key cellular processes. Although large amounts of data on the biochemical activities, dynamic behaviors, and important cellular functions of plant actin filaments have accumulated, their structural basis remains elusive. Here, we report a 3.9 Å structure of the plant actin filament from Zea mays pollen (ZMPA) using cryo-electron microscopy. The structure shows a right-handed, double-stranded (two parallel strands) and staggered architecture that is stabilized by intra- and interstrand interactions. While the overall structure resembles that of other actin filaments, its DNase I binding loop bends farther outward, adopting an open conformation similar to that of the jasplakinolide- or beryllium fluoride (BeF x )-stabilized rabbit skeletal muscle actin (RSMA) filament. Single-molecule magnetic tweezers analysis revealed that the ZMPA filament can resist a greater stretching force than the RSMA filament. Overall, these data provide evidence that plant actin filaments have greater stability than animal actin filaments, which might be important to their role as tracks for long-distance vesicle and organelle transportation.plantcell;31/12/2855/FX1F1fx1.
Organizational Affiliation:
Key Laboratory of Cell Proliferation and Regulation Biology of Ministry of Education, Center for Biological Science and Technology, College of Life Sciences, Beijing Normal University, Zhuhai 519087, China feisun@ibp.ac.cn hren@bnu.edu.cn.