Nanobodies: site-specific labeling for super-resolution imaging, rapid epitope-mapping and native protein complex isolation.
Pleiner, T., Bates, M., Trakhanov, S., Lee, C.T., Schliep, J.E., Chug, H., Bohning, M., Stark, H., Urlaub, H., Gorlich, D.(2015) Elife 4: e11349-e11349
- PubMed: 26633879
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.11349
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
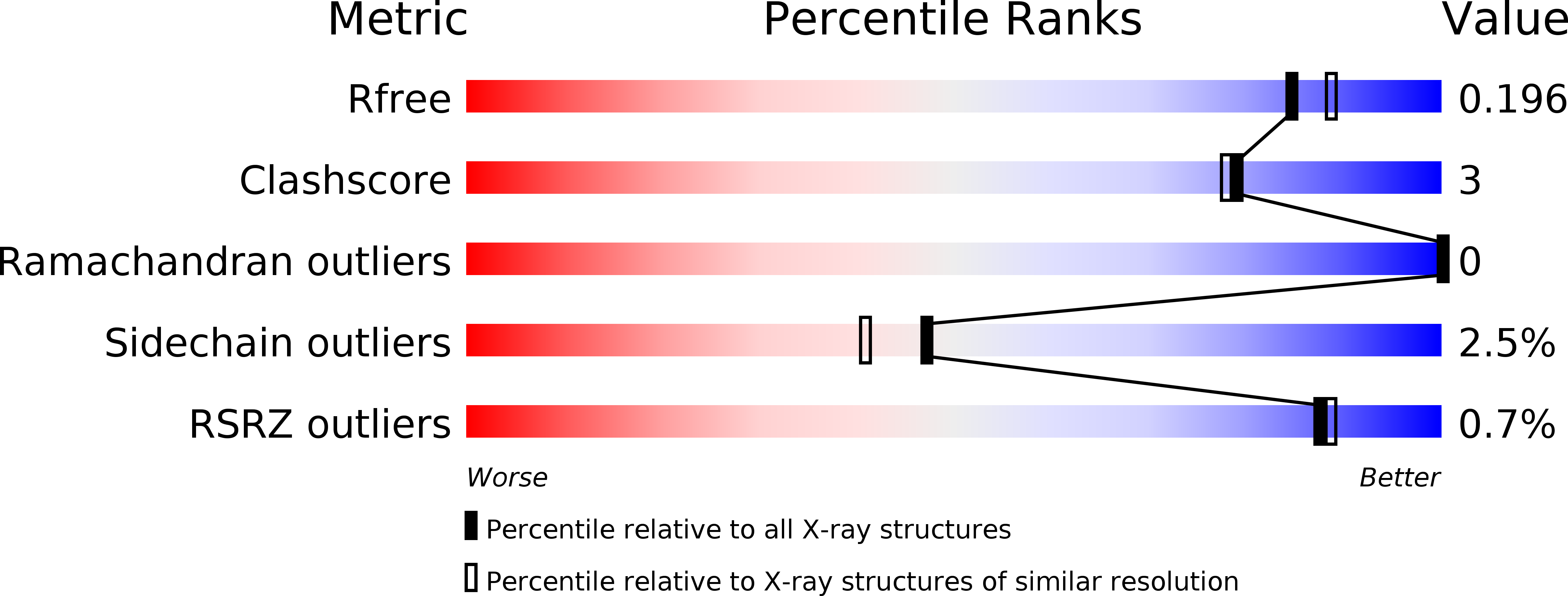
5E0Q - PubMed Abstract:
Nanobodies are single-domain antibodies of camelid origin. We generated nanobodies against the vertebrate nuclear pore complex (NPC) and used them in STORM imaging to locate individual NPC proteins with <2 nm epitope-label displacement. For this, we introduced cysteines at specific positions in the nanobody sequence and labeled the resulting proteins with fluorophore-maleimides. As nanobodies are normally stabilized by disulfide-bonded cysteines, this appears counterintuitive. Yet, our analysis showed that this caused no folding problems. Compared to traditional NHS ester-labeling of lysines, the cysteine-maleimide strategy resulted in far less background in fluorescence imaging, it better preserved epitope recognition and it is site-specific. We also devised a rapid epitope-mapping strategy, which relies on crosslinking mass spectrometry and the introduced ectopic cysteines. Finally, we used different anti-nucleoporin nanobodies to purify the major NPC building blocks – each in a single step, with native elution and, as demonstrated, in excellent quality for structural analysis by electron microscopy. The presented strategies are applicable to any nanobody and nanobody-target.
Organizational Affiliation:
Department of Cellular Logistics, Max Planck Institute for Biophysical Chemistry, Göttingen, Germany.