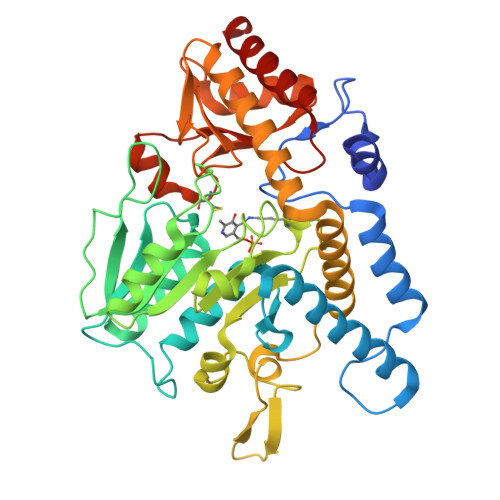
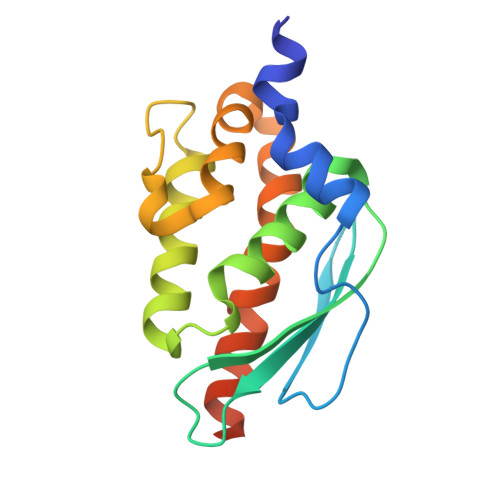
Feedback regulation of iron-sulfur cluster biogenesis.
Stuteley, S.M., Chen, J., Wang, J., Dawes, S., Baker, E.N., Squire, C.J., Pandelia, M.E., Bashiri, G.(2025) bioRxiv
- PubMed: 40667192
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1101/2025.06.15.659787
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
9DCL, 9DDD - PubMed Abstract:
Iron-sulfur (Fe-S) clusters are ubiquitous cofactors in biological systems. Given their central role in bacterial metabolism and pathogenesis, the biogenesis of Fe-S clusters is tightly controlled. We reveal a feedback regulatory mechanism involving the sulfide producing SufS/SufU complex within the sulfur utilization (SUF) system of Mycobacterium tuberculosis , the bacterium that causes tuberculosis. In this mechanism, [2Fe-2S] clusters compete with zinc ions for binding to the sulfide transfer protein SufU. Cluster binding induces SufU tetramerization, which prevents its interaction with the cysteine desulfurase SufS, thereby inhibiting SufS activation and limiting sulfide supply for Fe-S cluster biogenesis. These findings uncover an unrecognized regulatory mechanism in M. tuberculosis , ensuring strict control of Fe-S cluster production.