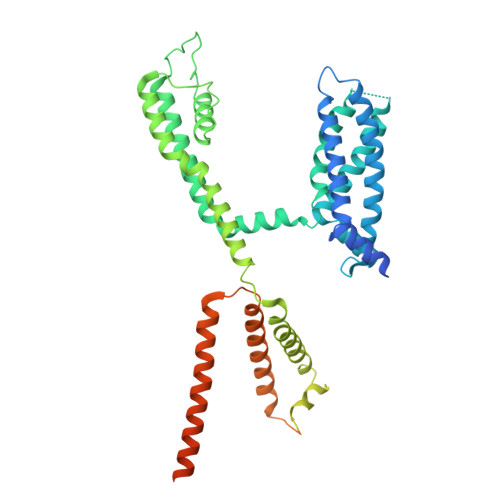
Mechanisms of KCNQ1 gating modulation by KCNE1/3 for cell-specific function.
Cui, C., Zhao, L., Kermani, A.A., Du, S., Pipatpolkai, T., Jiang, M., Chittori, S., Tan, Y.Z., Shi, J., Delemotte, L., Cui, J., Sun, J.(2025) Cell Res 35: 876-886
- PubMed: 40745202
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41422-025-01152-1
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
9VEC, 9VEI, 9VEN, 9VEO, 9WD8 - PubMed Abstract:
KCNQ1 potassium channels are essential for physiological processes such as cardiac rhythm and intestinal chloride secretion. KCNE family subunits (KCNE1-5) associate with KCNQ1, conferring distinct properties across various tissues. KCNQ1 activation requires membrane depolarization and phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2) whose cellular levels are controlled by Gαq-coupled GPCR activation. While modulation of KCNQ1's voltage-dependent activation by KCNE1/3 is well-characterized, their effects on PIP2-dependent gating of KCNQ1 via GPCR signaling remain less understood. Here we resolved structures of KCNQ1-KCNE1 and reassessed the reported KCNQ1-KCNE3 structures with and without PIP2. We revealed that KCNQ1-KCNE1/3 complexes feature two PIP2-binding sites, with KCNE1/3 contributing to a previously overlooked, uncharacterized site involving residues critical for coupling voltage sensor and pore domains. Via this site, KCNE1 and KCNE3 distinctly modulate the PIP2-dependent gating, in addition to the voltage sensitivity, of KCNQ1. Consequently, KCNE3 converts KCNQ1 into a voltage-insensitive PIP2-gated channel governed by GPCR signaling to maintain ion homeostasis in non-excitable cells. KCNE1, by significantly enhancing KCNQ1's PIP2 affinity and resistance to GPCR regulation, forms predominantly voltage-gated channels with KCNQ1 for conducting the slow-delayed rectifier current in excitable cardiac cells. Our study highlights how KCNE1/3 modulates KCNQ1 gating in different cellular contexts, providing insights into tissue-specifically targeting multi-functional channels.
- Department of Biological Sciences, National University of Singapore, Singapore, Singapore.
Organizational Affiliation: