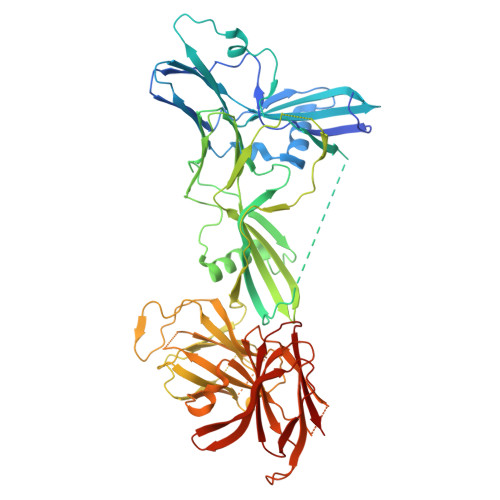
Structure of the complete 14-subunit botulinum neurotoxin B complex reveals a unique anchoring through the narrow central pore of HA70.
Krc, A., Kosenina, S.P., Nowakowska, M.B., Masuyer, G., Stenmark, P.(2025) Sci Adv 11: eadx5058-eadx5058
- PubMed: 40864696
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.adx5058
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
9QC7, 9QC8, 9QCE, 9QCM, 9QCN, 9QCO - PubMed Abstract:
Botulinum neurotoxin serotype B1 (BoNT/B) is a highly potent neurotoxin and therapeutic agent. Here, we present the structure of the complete 14-subunit (780 kDa) progenitor toxin complex (L-PTC) and of five subcomplexes. The structures show how the toxin interacts with its associated components in their role to protect and deliver BoNT/B across epithelial barriers. Each subcomplex, including the M-PTC, M-PTC-HA70, NTNH-HA70, and HA70 trimer, provides detailed understanding of the assembly mechanism, in which the NTNH-nLoop adopts a unique fold that locks the M-PTC into a central pore formed by HA70. The HA subcomplex presents a tripod architecture with flexible legs that may adapt to the rugged cell surface. Mass photometry reveals the pH dependence of BoNT/B release from the complex which is unexpectedly influenced by the presence of HA70. This study provides the complete L-PTC structure, offering insights into its assemblage and supporting the development of countermeasures and therapeutic applications.
- Department of Biochemistry and Biophysics, Stockholm University, Stockholm, Sweden.
Organizational Affiliation: