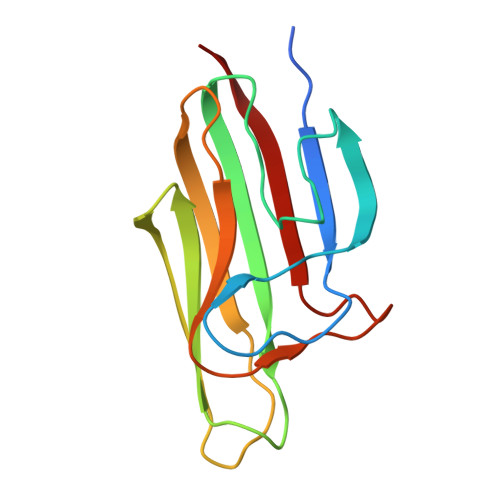
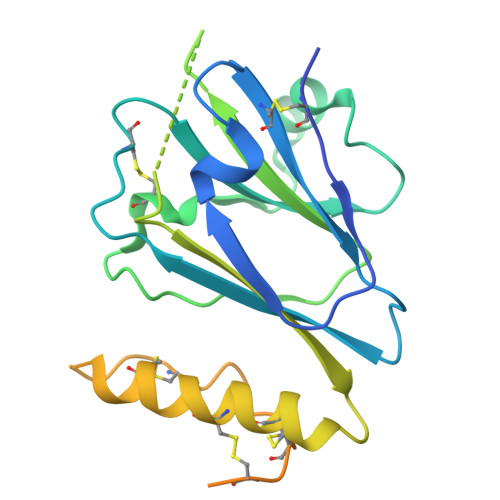
Structural basis of calcium-dependent C1ql1/BAI3 assemblies in synaptic connectivity.
Liao, L., Han, Y., Niu, F., Wang, Y., Lu, Y., Xu, S., Zhu, H., Lin, L., Xiao, J., Tou, H.I., Gao, J., Zhang, B., Wei, Z.(2025) Nat Commun 16: 11444-11444
- PubMed: 41372137
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-025-66254-1
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
9LKK, 9LKL, 9LKM - PubMed Abstract:
Cell adhesion molecules (CAMs) are pivotal in establishing and maintaining synaptic connectivity. Emerging evidence indicates that some secreted factors within the synaptic cleft, including C1q-like proteins (C1qls), play a crucial role in bridging pre- and post-synapses by connecting the bilateral CAMs. However, the mechanisms of those secreted factors in synapse assembly remain incomplete. Here, we explore C1ql-mediated synaptic connectivity, focusing on the assembly of C1ql1 and its postsynaptic receptor brain-specific angiogenesis inhibitor 3 (BAI3, also called ADGRB3). Our biochemical, structural, and computational analyses reveal that the trimeric globular C1q (gC1q) domain of C1ql1 undergoes a calcium-modulated domain-swapping event to form a hexamer. Cryo-EM study manifests the stabilizing role of calcium ions on the C1ql1_gC1q hexamer in complex with the extended CUB domain of BAI3. Using the gC1q hexamer, full-length C1ql1 further assembles into linear clusters, possibly providing a scaffold to accumulate BAI3 receptors on the plasma membrane. Our cellular and in vivo studies support a role for the gC1q-mediated dynamic assembly of C1ql1 in receptor accumulation and synapse maintenance. Collectively, our findings provide a plausible mechanism of secreted factor-mediated synaptic connectivity, driven by the calcium-modulated assembly of C1qls and their interactions with CAMs.
- Shenzhen Key Laboratory of Biomolecular Assembling and Regulation, Shenzhen, Guangdong, China.
Organizational Affiliation: