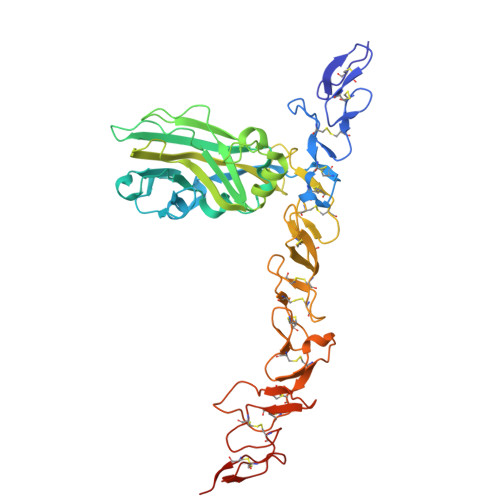
Structural insights on perlecan and Schwartz-Jampel syndrome.
Sohail, A.A., Koski, M.K., Ruddock, L.W.(2025) Matrix Biol 138: 1-7
- PubMed: 40118124
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matbio.2025.03.002
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
9I5A, 9I5B - PubMed Abstract:
Perlecan is an essential multi-domain, disulfide bond rich basement membrane protein. Mutations in perlecan cause Schwartz-Jampel syndrome and dyssegmental dysplasia. While there has been a large body of experimental work reported on perlecan, there is only minimal structural information available to date. There is no prior structural data for region 3 of perlecan in which some Schwartz-Jampel syndrome causing point mutations have been reported. Here, we produce constructs of the disulfide rich region 3 of perlecan along with five mutations previously reported to cause Schwatz-Jampel syndrome. Four of the mutations resulted in decreased yields and thermal stability compared to the wild-type protein. In contrast, the P1019L mutation was produced in good yields and showed higher thermal stability than the wild-type protein. The crystal structures for both the wild-type and P1019L mutation were solved. As expected, both showed laminin IV-like and laminin-type EGF-like domains, with the P1019L mutation resulting in only a minor conformational change in a loop region and no significant changes in regular secondary or tertiary structure.
- Faculty of Biochemistry and Molecular Medicine, University of Oulu, Oulu, 90220, Finland.
Organizational Affiliation: