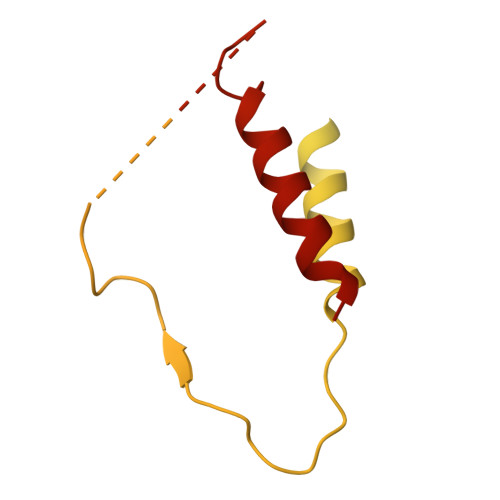
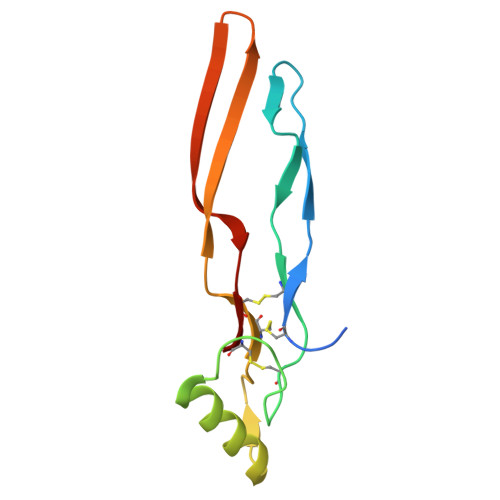
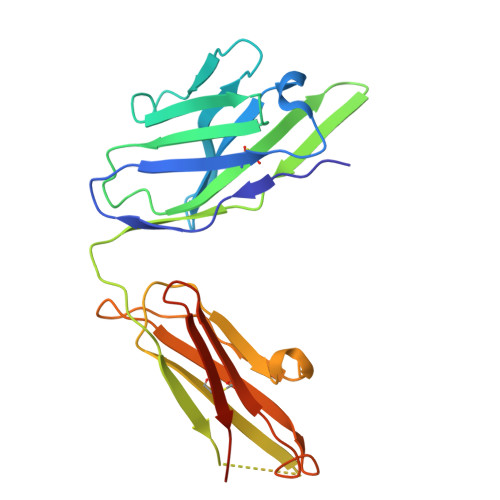
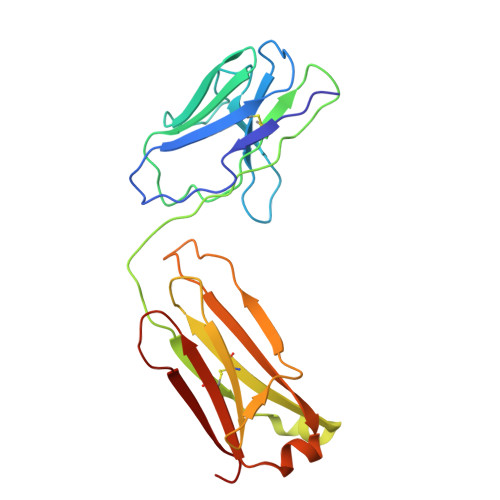
A divergent two-domain structure of the anti-Mullerian hormone prodomain.
Howard, J.A., Hok, L., Cate, R.L., Sanford, N.J., Hart, K.N., Leach, E.A.E., Bruening, A.S., Nagykery, N., Donahoe, P.K., Pepin, D., Thompson, T.B.(2025) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 122: e2418088122-e2418088122
- PubMed: 39805014
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2418088122
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
9BAN, 9BAO - PubMed Abstract:
TGFβ family ligands are synthesized as precursors consisting of an N-terminal prodomain and C-terminal growth factor (GF) signaling domain. After proteolytic processing, the prodomain typically remains noncovalently associated with the GF, sometimes forming a high-affinity latent procomplex that requires activation. For the TGFβ family ligand anti-Müllerian hormone (AMH), the prodomain maintains a high-affinity interaction with its GF that does not render it latent. While the prodomain can be displaced by the type II receptor, AMHR2, the nature of the GF:prodomain interaction and the mechanism of prodomain displacement by AMHR2 are currently unknown. We show here that the AMH prodomain exhibits an atypical two-domain structure, containing a dimerizing and a GF-binding domain connected through a flexible linker. Cryo-EM and genomic analyses show that the distinctive GF-binding domain, the result of an exon insertion 450 Mya, comprises a helical bundle and a belt-like structure which interact with the GF at the type II and I receptor binding sites, respectively. The dimerizing domain, which adopts a TGFβ-like propeptide fold, covalently connects two prodomains through intermolecular disulfide bonds. Disease mutations map to both the GF-binding and dimerization domains. Our results support a model where AMHR2 displaces the helical bundle and induces a conformational change in the GF, followed by release of the prodomain and engagement of the type I receptor. Collectively, this study shows that the AMH prodomain has evolved an atypical binding interaction with the GF that favors, without disrupting signaling, the maintenance of a noncovalent complex until receptors are engaged.
- Department of Pharmacology, Physiology, and Neurobiology, University of Cincinnati, Cincinnati, OH 45267.
Organizational Affiliation: