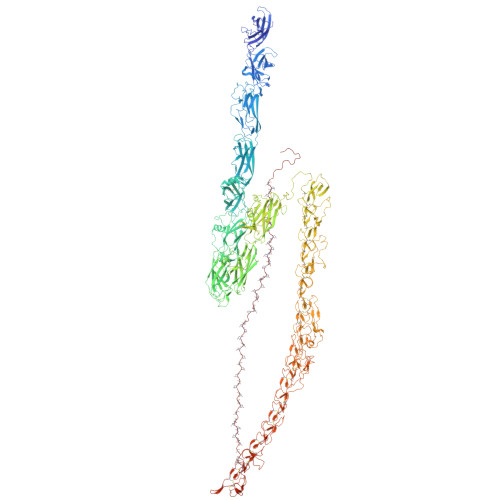Mastigoneme structure reveals insights into the O-linked glycosylation code of native hydroxyproline-rich helices.
Dai, J., Ma, M., Niu, Q., Eisert, R.J., Wang, X., Das, P., Lechtreck, K.F., Dutcher, S.K., Zhang, R., Brown, A.(2024) Cell
- PubMed: 38552624
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2024.03.005
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
9B4H - PubMed Abstract:
Hydroxyproline-rich glycoproteins (HRGPs) are a ubiquitous class of protein in the extracellular matrices and cell walls of plants and algae, yet little is known of their native structures or interactions. Here, we used electron cryomicroscopy (cryo-EM) to determine the structure of the hydroxyproline-rich mastigoneme, an extracellular filament isolated from the cilia of the alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. The structure demonstrates that mastigonemes are formed from two HRGPs (a filament of MST1 wrapped around a single copy of MST3) that both have hyperglycosylated poly(hydroxyproline) helices. Within the helices, O-linked glycosylation of the hydroxyproline residues and O-galactosylation of interspersed serine residues create a carbohydrate casing. Analysis of the associated glycans reveals how the pattern of hydroxyproline repetition determines the type and extent of glycosylation. MST3 possesses a PKD2-like transmembrane domain that forms a heteromeric polycystin-like cation channel with PKD2 and SIP, explaining how mastigonemes are tethered to ciliary membranes.
- Department of Biological Chemistry and Molecular Pharmacology, Blavatnik Institute, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: