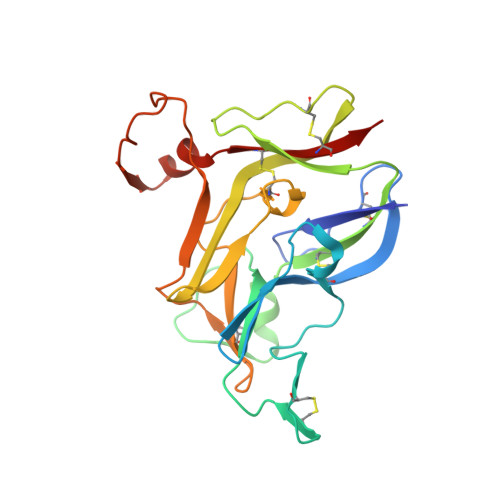
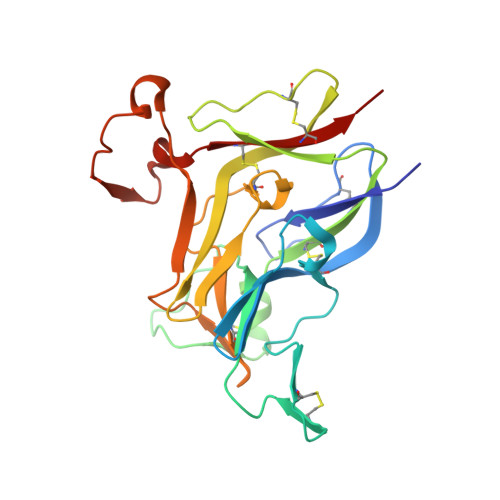
Collagen IV of basement membranes: IV. Adaptive mechanism of collagen IV scaffold assembly in Drosophila.
Summers, J.A., Yarbrough, M., Liu, M., McDonald, W.H., Hudson, B.G., Pastor-Pareja, J.C., Boudko, S.P.(2023) J Biological Chem 299: 105394-105394
- PubMed: 37890775
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbc.2023.105394
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8TXN, 8TYS - PubMed Abstract:
Collagen IV is an essential structural protein in all metazoans. It provides a scaffold for the assembly of basement membranes, a specialized form of extracellular matrix, which anchors and signals cells and provides microscale tensile strength. Defective scaffolds cause basement membrane destabilization and tissue dysfunction. Scaffolds are composed of α-chains that coassemble into triple-helical protomers of distinct chain compositions, which in turn oligomerize into supramolecular scaffolds. Chloride ions mediate the oligomerization via NC1 trimeric domains, forming an NC1 hexamer at the protomer-protomer interface. The chloride concentration-"chloride pressure"-on the outside of cells is a primordial innovation that drives the assembly and dynamic stabilization of collagen IV scaffolds. However, a Cl-independent mechanism is operative in Ctenophora, Ecdysozoa, and Rotifera, which suggests evolutionary adaptations to environmental or tissue conditions. An understanding of these exceptions, such as the example of Drosophila, could shed light on the fundamentals of how NC1 trimers direct the oligomerization of protomers into scaffolds. Here, we investigated the NC1 assembly of Drosophila. We solved the crystal structure of the NC1 hexamer, determined the chain composition of protomers, and found that Drosophila adapted an evolutionarily unique mechanism of scaffold assembly that requires divalent cations. By studying the Drosophila case we highlighted the mechanistic role of chloride pressure for maintaining functionality of the NC1 domain in humans. Moreover, we discovered that the NC1 trimers encode information for homing protomers to distant tissue locations, providing clues for the development of protein replacement therapy for collagen IV genetic diseases.
- Aspirnaut Program, Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, Tennessee, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: