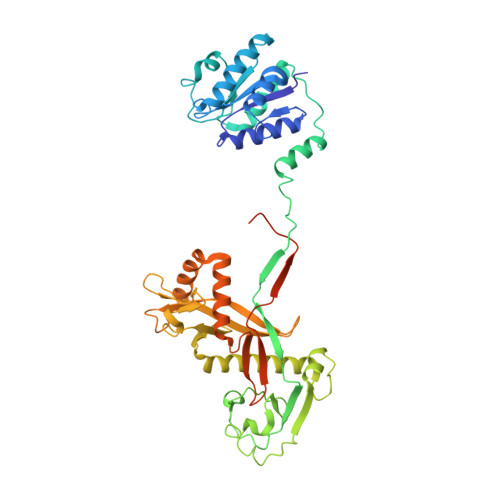
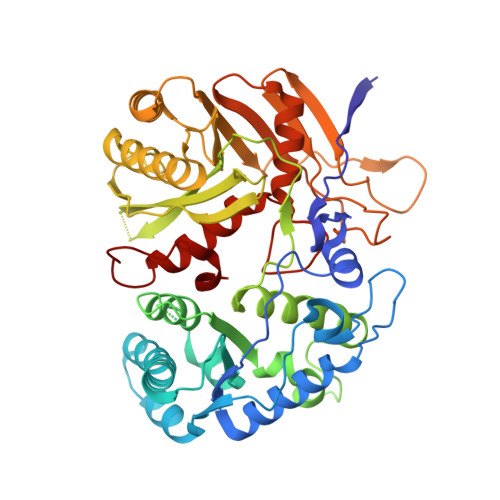
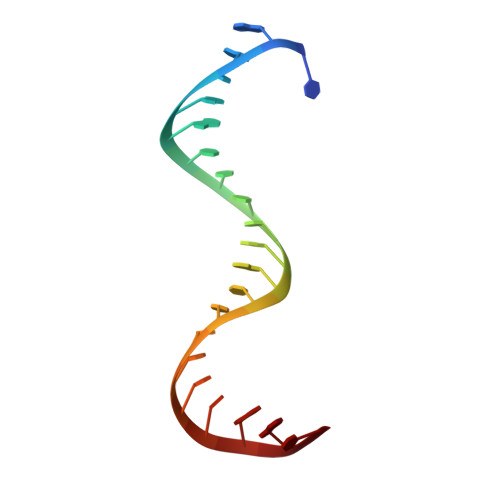
Target DNA-dependent activation mechanism of the prokaryotic immune system SPARTA.
Finocchio, G., Koopal, B., Potocnik, A., Heijstek, C., Westphal, A.H., Jinek, M., Swarts, D.C.(2024) Nucleic Acids Res 52: 2012-2029
- PubMed: 38224450
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkad1248
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8QLO, 8QLP - PubMed Abstract:
In both prokaryotic and eukaryotic innate immune systems, TIR domains function as NADases that degrade the key metabolite NAD+ or generate signaling molecules. Catalytic activation of TIR domains requires oligomerization, but how this is achieved varies in distinct immune systems. In the Short prokaryotic Argonaute (pAgo)/TIR-APAZ (SPARTA) immune system, TIR NADase activity is triggered upon guide RNA-mediated recognition of invading DNA by an unknown mechanism. Here, we describe cryo-EM structures of SPARTA in the inactive monomeric and target DNA-activated tetrameric states. The monomeric SPARTA structure reveals that in the absence of target DNA, a C-terminal tail of TIR-APAZ occupies the nucleic acid binding cleft formed by the pAgo and TIR-APAZ subunits, inhibiting SPARTA activation. In the active tetrameric SPARTA complex, guide RNA-mediated target DNA binding displaces the C-terminal tail and induces conformational changes in pAgo that facilitate SPARTA-SPARTA dimerization. Concurrent release and rotation of one TIR domain allow it to form a composite NADase catalytic site with the other TIR domain within the dimer, and generate a self-complementary interface that mediates cooperative tetramerization. Combined, this study provides critical insights into the structural architecture of SPARTA and the molecular mechanism underlying target DNA-dependent oligomerization and catalytic activation.
- Department of Biochemistry, University of Zurich, 8057 Zurich, Switzerland.
Organizational Affiliation: