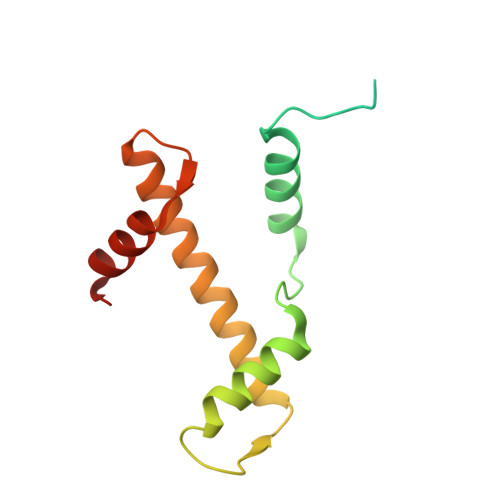
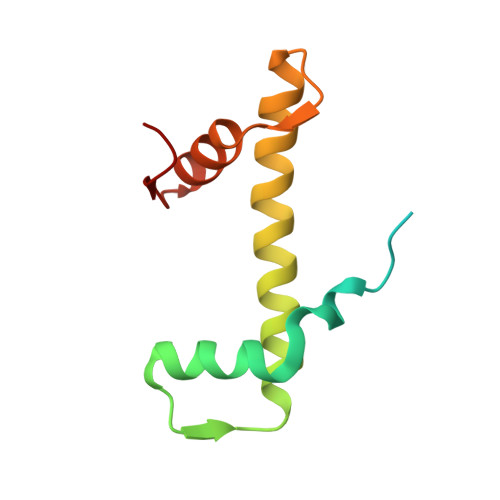
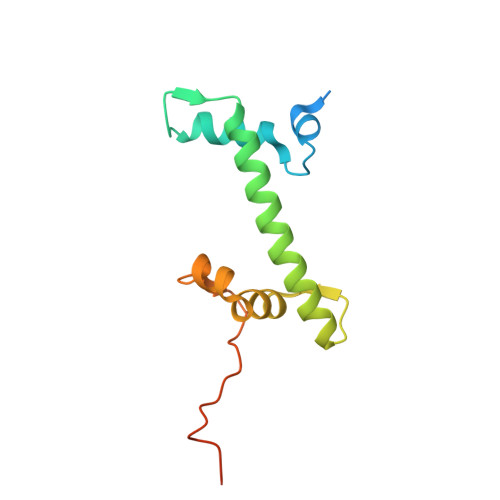
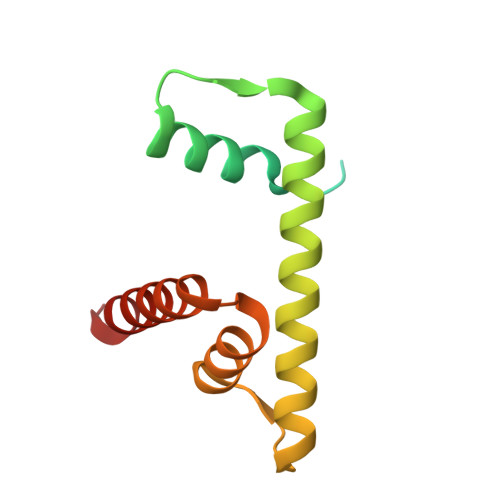
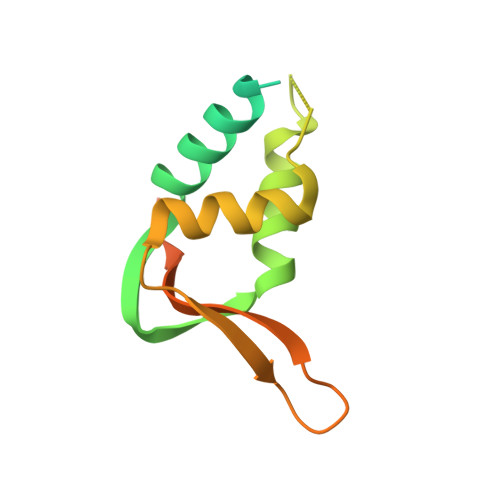
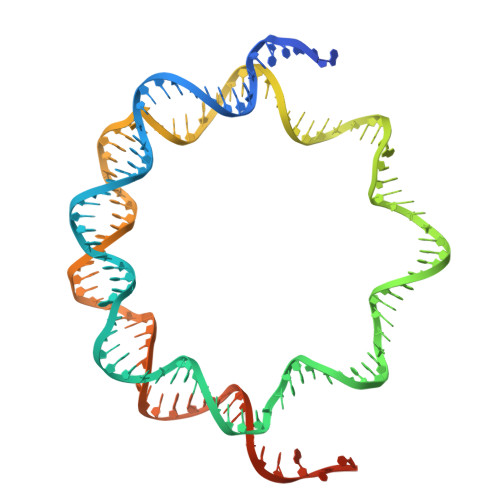
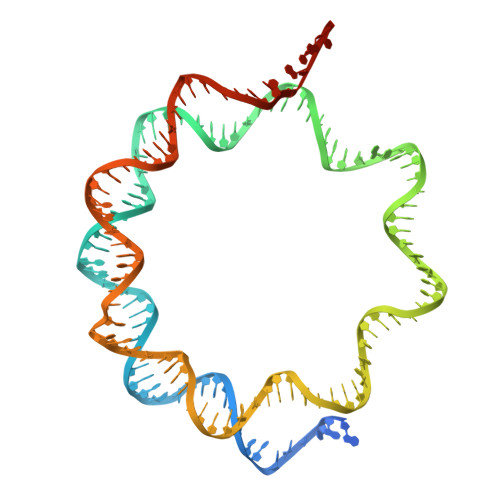
Structural basis of nucleosome binding and destabilization by the extended DNA binding domain of RFX5.
Xue, W., Han, Y., Tian, Y., Wang, J., Xie, Z., Zheng, X., Yue, X., Dong, S., Li, H., Luo, Z., Zhang, S., Yang, Y., Zou, Z., Li, W., Ma, N., Zhu, F., Chen, C., Yin, Y., Zhang, Y., Xu, K.(2025) Nucleic Acids Res 53
- PubMed: 40744500
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkaf734
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8ZJR, 8ZJT - PubMed Abstract:
Among the regulatory factor X (RFX) transcription factor family, RFX5 is uniquely reported to bind nucleosomes and induce nucleosome remodeling in vivo. Dysfunctions in RFX5 have been implicated in various diseases. Here, we present the cryogenic electron microscopy (cryo-EM) structure of the RFX5-nucleosome complex, revealing that the extended DNA binding domain (eDBD) of RFX5 binds to the nucleosome at superhelical location +2. RFX5 eDBD engages not only with nucleosomal DNA but also with histones through extensive interactions. Compared to the structure of a free nucleosome, RFX5 eDBD induces localized distortion of the bound DNA gyre and detachment of the adjacent DNA gyre in the RFX5-nucleosome complex. This structural alteration could potentially increase DNA accessibility and enhance transcriptional activity in vivo. Overall, our study provides novel insights into the mechanisms by which RFX5 eDBD interacts with and destabilizes nucleosomes.
- Shanghai Key Laboratory of Anesthesiology and Brain Functional Modulation, Clinical Research Center for Anesthesiology and Perioperative Medicine, Translational Research Institute of Brain and Brain-Like Intelligence, Shanghai Fourth People's Hospital, School of Medicine, Tongji University, Shanghai 200434, China.
Organizational Affiliation: