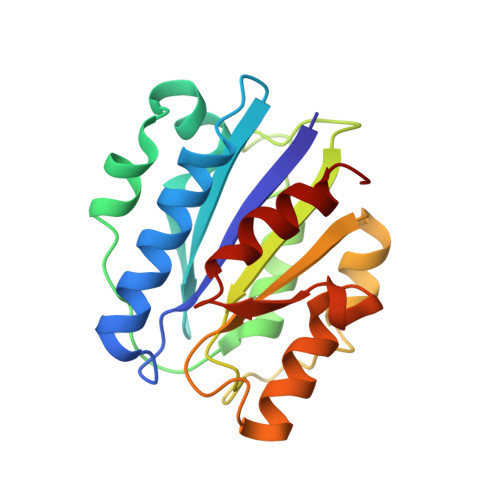
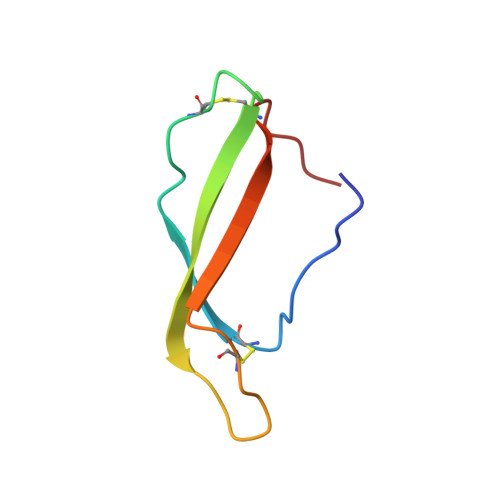
alpha M I-domain of integrin Mac-1 binds the cytokine pleiotrophin using multiple mechanisms.
Nguyen, H., Podolnikova, N.P., Ugarova, T.P., Wang, X.(2024) Structure 32: 1184-1196.e4
- PubMed: 38729161
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.str.2024.04.013
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8VOH, 8VOI - PubMed Abstract:
The integrin Mac-1 (α M β 2 , CD11b/CD18, CR3) is an adhesion receptor expressed on macrophages and neutrophils. Mac-1 is also a promiscuous integrin that binds a diverse set of ligands through its α M I-domain. However, the binding mechanism of most ligands remains unclear. We have characterized the interaction of α M I-domain with the cytokine pleiotrophin (PTN), a protein known to bind α M I-domain and induce Mac-1-mediated cell adhesion and migration. Our data show that PTN's N-terminal domain binds a unique site near the N- and C-termini of the α M I-domain using a metal-independent mechanism. However, a stronger interaction is achieved when an acidic amino acid in a zwitterionic motif in PTN's C-terminal domain chelates the divalent cation in the metal ion-dependent adhesion site of active α M I-domain. These results indicate that α M I-domain can bind ligands using multiple mechanisms and that the active α M I-domain has a preference for motifs containing both positively and negatively charged amino acids.
- School of Molecular Sciences, Arizona State University, Tempe, AZ 85281, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: