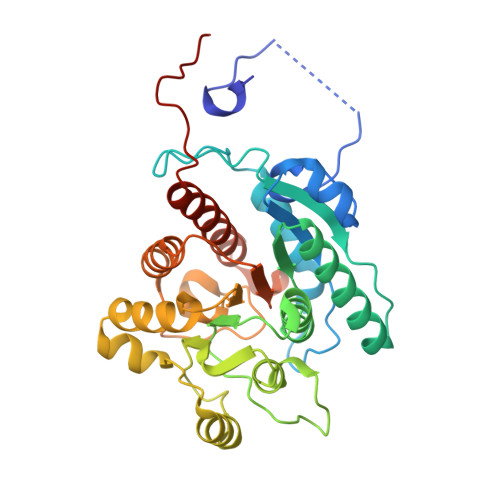
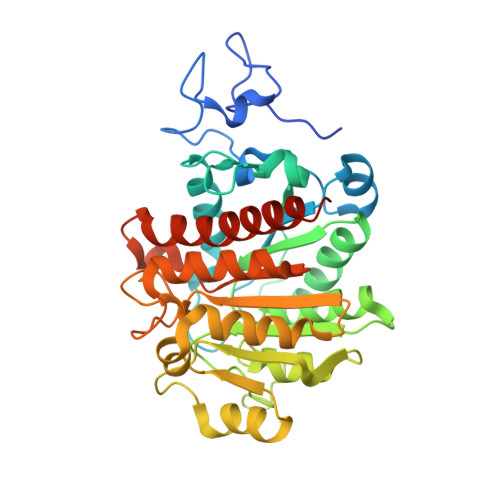
Dinickel enzyme evolved to metabolize the pharmaceutical metformin and its implications for wastewater and human microbiomes.
Tassoulas, L.J., Rankin, J.A., Elias, M.H., Wackett, L.P.(2024) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 121: e2312652121-e2312652121
- PubMed: 38408229
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2312652121
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8SNF, 8SNK, 8SP2 - PubMed Abstract:
Metformin is the first-line treatment for type II diabetes patients and a pervasive pollutant with more than 180 million kg ingested globally and entering wastewater. The drug's direct mode of action is currently unknown but is linked to effects on gut microbiomes and may involve specific gut microbial reactions to the drug. In wastewater treatment plants, metformin is known to be transformed by microbes to guanylurea, although genes encoding this metabolism had not been elucidated. In the present study, we revealed the function of two genes responsible for metformin decomposition ( mfmA and mfmB ) found in isolated bacteria from activated sludge. MfmA and MfmB form an active heterocomplex (MfmAB) and are members of the ureohydrolase protein superfamily with binuclear metal-dependent activity. MfmAB is nickel-dependent and catalyzes the hydrolysis of metformin to dimethylamine and guanylurea with a catalytic efficiency (k cat /K M ) of 9.6 × 10 3 M -1 s -1 and K M for metformin of 0.82 mM. MfmAB shows preferential activity for metformin, being able to discriminate other close substrates by several orders of magnitude. Crystal structures of MfmAB show coordination of binuclear nickel bound in the active site of the MfmA subunit but not MfmB subunits, indicating that MfmA is the active site for the MfmAB complex. Mutagenesis of residues conserved in the MfmA active site revealed those critical to metformin hydrolase activity and its small substrate binding pocket allowed for modeling of bound metformin. This study characterizes the products of the mfmAB genes identified in wastewater treatment plants on three continents, suggesting that metformin hydrolase is widespread globally in wastewater.
- Department of Biochemistry, Biophysics, and Molecular Biology, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, MN 55455.
Organizational Affiliation: