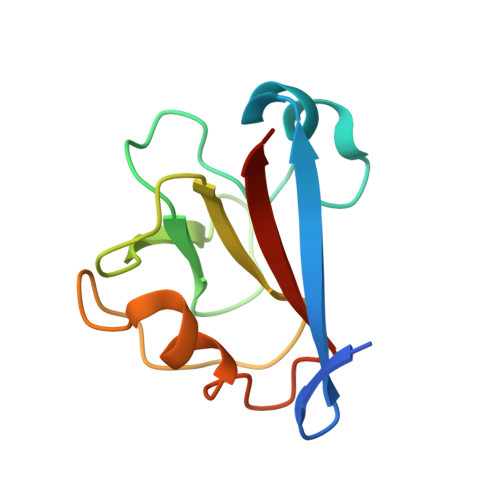
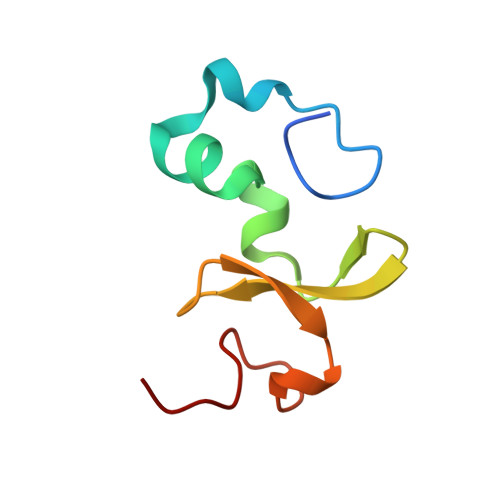
Bimodular architecture of bacterial effector SAP05 that drives ubiquitin-independent targeted protein degradation.
Liu, Q., Maqbool, A., Mirkin, F.G., Singh, Y., Stevenson, C.E.M., Lawson, D.M., Kamoun, S., Huang, W., Hogenhout, S.A.(2023) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 120: e2310664120-e2310664120
- PubMed: 38039272
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2310664120
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8PFC, 8PFD - PubMed Abstract:
In eukaryotes, targeted protein degradation (TPD) typically depends on a series of interactions among ubiquitin ligases that transfer ubiquitin molecules to substrates leading to degradation by the 26S proteasome. We previously identified that the bacterial effector protein SAP05 mediates ubiquitin-independent TPD. SAP05 forms a ternary complex via interactions with the von Willebrand Factor Type A (vWA) domain of the proteasomal ubiquitin receptor Rpn10 and the zinc-finger (ZnF) domains of the SQUAMOSA-PROMOTER BINDING PROTEIN-LIKE (SPL) and GATA BINDING FACTOR (GATA) transcription factors (TFs). This leads to direct TPD of the TFs by the 26S proteasome. Here, we report the crystal structures of the SAP05-Rpn10 vWA complex at 2.17 Å resolution and of the SAP05-SPL5 ZnF complex at 2.20 Å resolution. Structural analyses revealed that SAP05 displays a remarkable bimodular architecture with two distinct nonoverlapping surfaces, a "loop surface" with three protruding loops that form electrostatic interactions with ZnF, and a "sheet surface" featuring two β-sheets, loops, and α-helices that establish polar interactions with vWA. SAP05 binding to ZnF TFs involves single amino acids responsible for multiple contacts, while SAP05 binding to vWA is more stable due to the necessity of multiple mutations to break the interaction. In addition, positioning of the SAP05 complex on the 26S proteasome points to a mechanism of protein degradation. Collectively, our findings demonstrate how a small bacterial bimodular protein can bypass the canonical ubiquitin-proteasome proteolysis pathway, enabling ubiquitin-independent TPD in eukaryotic cells. This knowledge holds significant potential for the creation of TPD technologies.
- Department of Crop Genetics, John Innes Centre, Norwich Research Park, Norwich NR4 7UH, United Kingdom.
Organizational Affiliation: