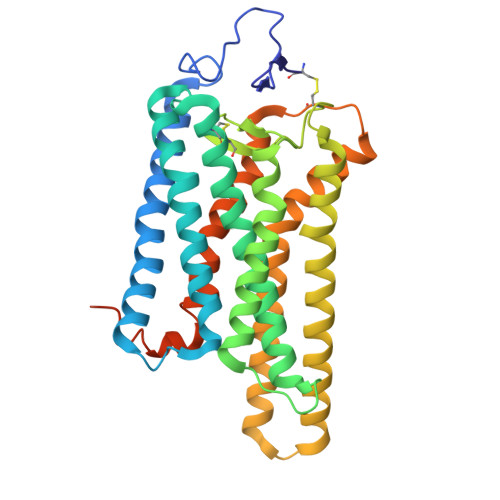
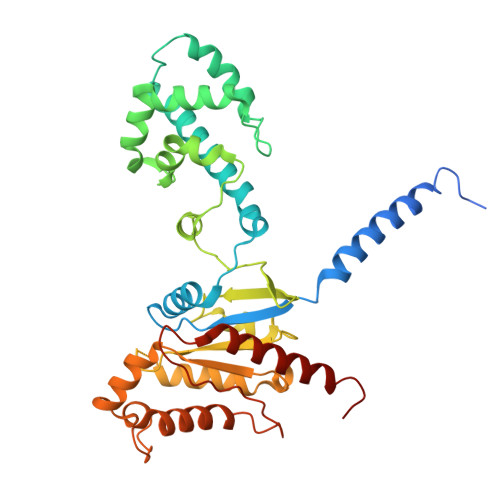
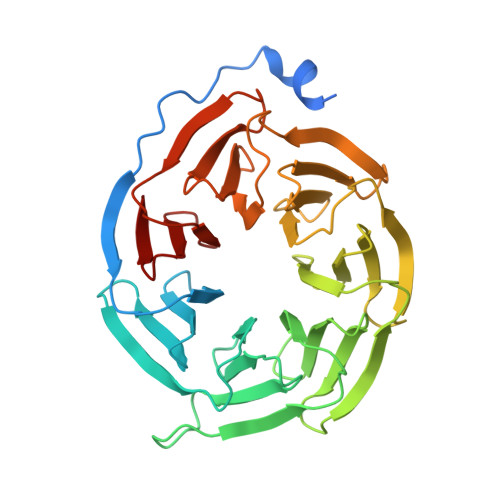
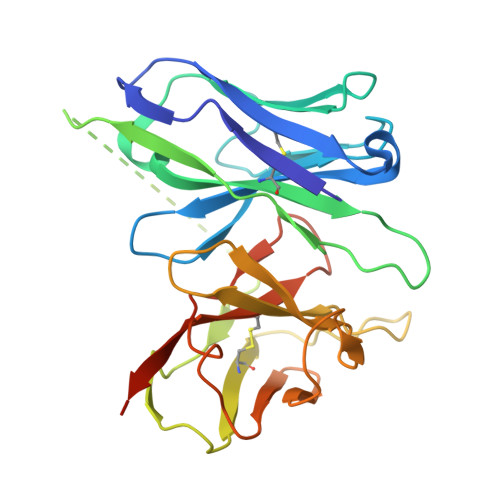
Tool antibody fragments reveal multiple conformations of the rhodopsin-Gi signaling complex.
Pamula, F., Tejero, O., Muhle, J., Thoma, R., Schertler, G.F.X., Marino, J., Tsai, C.J.(2025) Biophys J
- PubMed: 41029899
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bpj.2025.09.044
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8P12, 8P13, 8P15 - PubMed Abstract:
Antibody Fab fragments are widely used protein binders that assist in structural studies of G-protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) signaling complexes. Expanding the repertoire of such binders to target distinct components of the signaling complex offers opportunities to probe conformational regulation and dynamics. Here, we report the biochemical and cryo-EM characterization of two Fab fragments, Fab79 and Fab13, raised against the rhodopsin-Gαiβγ complex. Fab79 binds to the flexible α-helical domain (AHD) of the Gαi subunit and prevents complex dissociation in the presence of the nonhydrolyzable GTP analog, GTPγS, likely by hindering AHD closure, a step necessary for complex dissociation. In contrast, Fab13 binds rigidly to Gβ without directly contacting Gα or the receptor. These findings show that Fab79 and Fab13 reveal functionally relevant conformational states of G-protein activation and serve as practical tools to stabilize or modulate GPCR signaling complexes.
- Laboratory of Biomolecular Research, Paul Scherrer Institute, Villigen, Switzerland; Department of Biology, ETH Zürich, Zürich, Switzerland.
Organizational Affiliation: