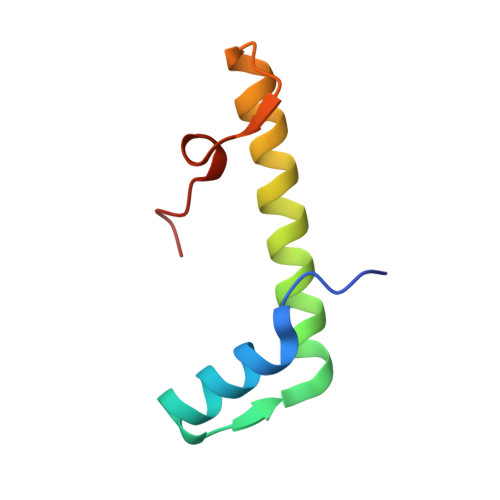
Histones with an unconventional DNA-binding mode in vitro are major chromatin constituents in the bacterium Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus.
Hocher, A., Laursen, S.P., Radford, P., Tyson, J., Lambert, C., Stevens, K.M., Montoya, A., Shliaha, P.V., Picardeau, M., Sockett, R.E., Luger, K., Warnecke, T.(2023) Nat Microbiol 8: 2006-2019
- PubMed: 37814071
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41564-023-01492-x
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8FVX, 8FW7 - PubMed Abstract:
Histone proteins bind DNA and organize the genomes of eukaryotes and most archaea, whereas bacteria rely on different nucleoid-associated proteins. Homology searches have detected putative histone-fold domains in a few bacteria, but whether these function like archaeal/eukaryotic histones is unknown. Here we report that histones are major chromatin components in the bacteria Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus and Leptospira interrogans. Patterns of sequence evolution suggest important roles for histones in additional bacterial clades. Crystal structures (<2.0 Å) of the B. bacteriovorus histone (Bd0055) dimer and the histone-DNA complex confirm conserved histone-fold topology but indicate a distinct DNA-binding mode. Unlike known histones in eukaryotes, archaea and viruses, Bd0055 binds DNA end-on, forming a sheath of dimers encasing straight DNA rather than wrapping DNA around their outer surface. Our results demonstrate that histones are present across the tree of life and highlight potential evolutionary innovation in how they associate with DNA.
- Medical Research Council London Institute of Medical Sciences, London, UK. a.hocher@lms.mrc.ac.uk.
Organizational Affiliation: