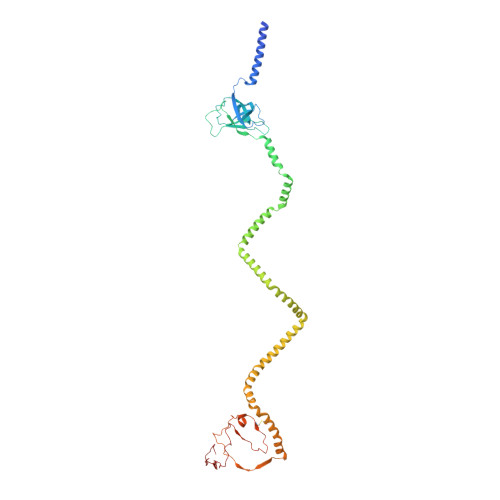
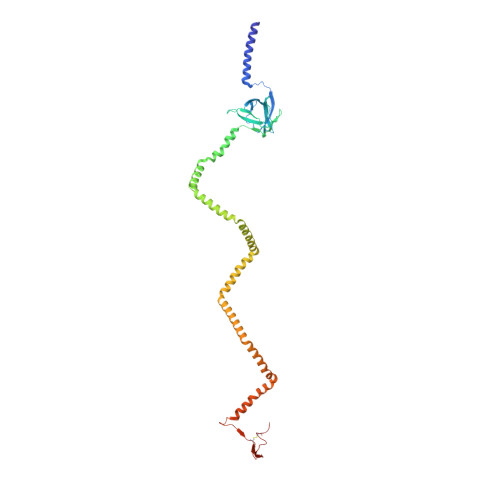
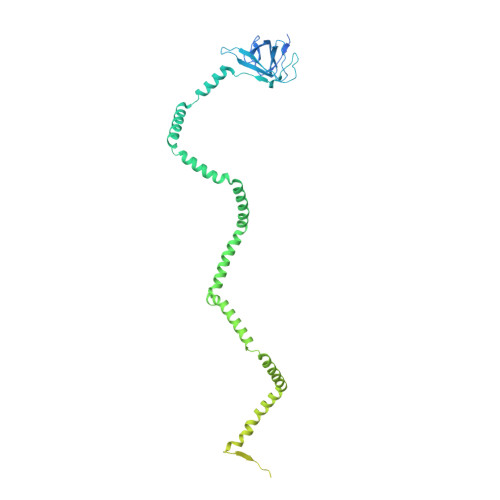
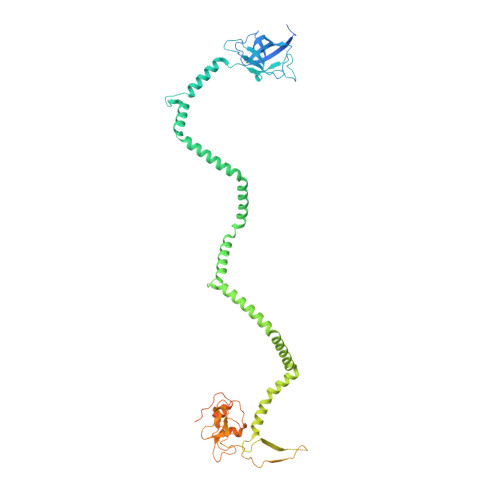
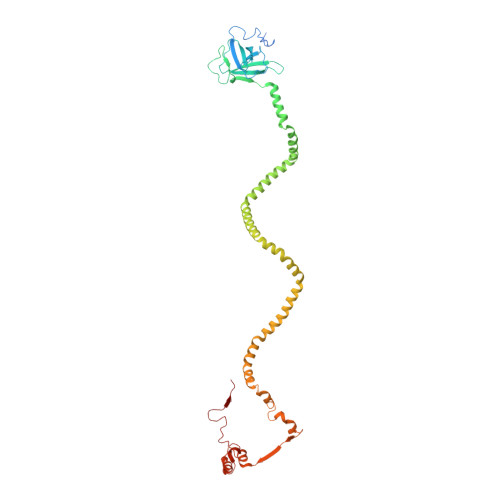
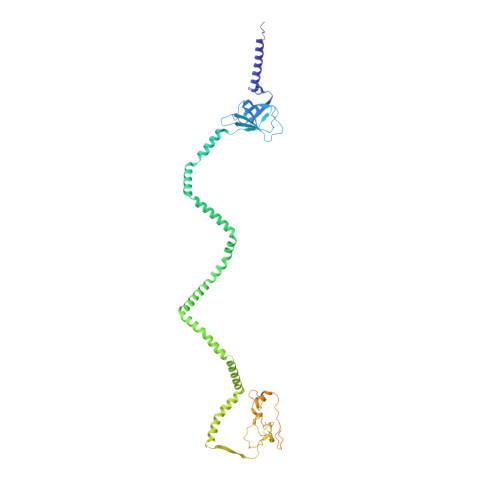
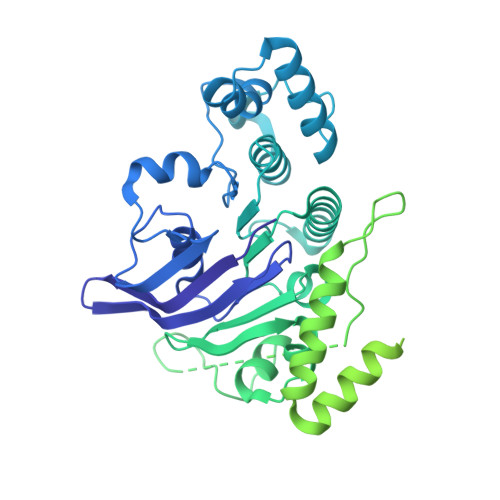
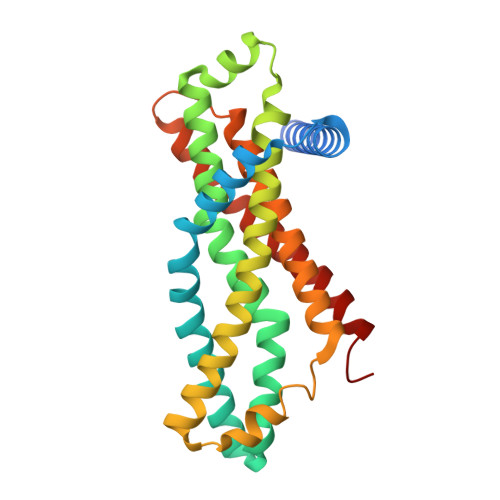
Structure of an endogenous mycobacterial MCE lipid transporter.
Chen, J., Fruhauf, A., Fan, C., Ponce, J., Ueberheide, B., Bhabha, G., Ekiert, D.C.(2023) Nature 620: 445-452
- PubMed: 37495693
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-023-06366-0
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8FED, 8FEE, 8FEF - PubMed Abstract:
To replicate inside macrophages and cause tuberculosis, Mycobacterium tuberculosis must scavenge a variety of nutrients from the host 1,2 . The mammalian cell entry (MCE) proteins are important virulence factors in M. tuberculosis 1,3 , where they are encoded by large gene clusters and have been implicated in the transport of fatty acids 4-7 and cholesterol 1,4,8 across the impermeable mycobacterial cell envelope. Very little is known about how cargos are transported across this barrier, and it remains unclear how the approximately ten proteins encoded by a mycobacterial mce gene cluster assemble to transport cargo across the cell envelope. Here we report the cryo-electron microscopy (cryo-EM) structure of the endogenous Mce1 lipid-import machine of Mycobacterium smegmatis-a non-pathogenic relative of M. tuberculosis. The structure reveals how the proteins of the Mce1 system assemble to form an elongated ABC transporter complex that is long enough to span the cell envelope. The Mce1 complex is dominated by a curved, needle-like domain that appears to be unrelated to previously described protein structures, and creates a protected hydrophobic pathway for lipid transport across the periplasm. Our structural data revealed the presence of a subunit of the Mce1 complex, which we identified using a combination of cryo-EM and AlphaFold2, and name LucB. Our data lead to a structural model for Mce1-mediated lipid import across the mycobacterial cell envelope.
- Department of Cell Biology, New York University School of Medicine, New York, NY, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: