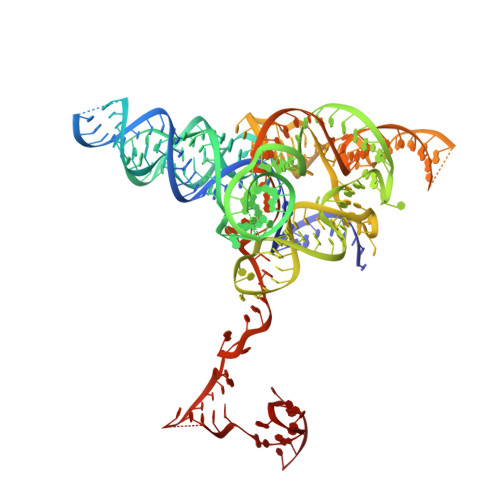
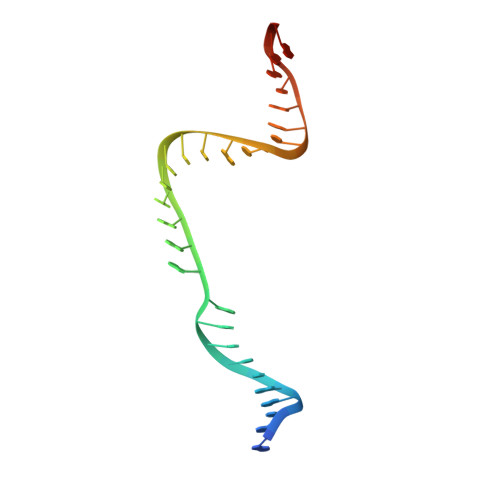
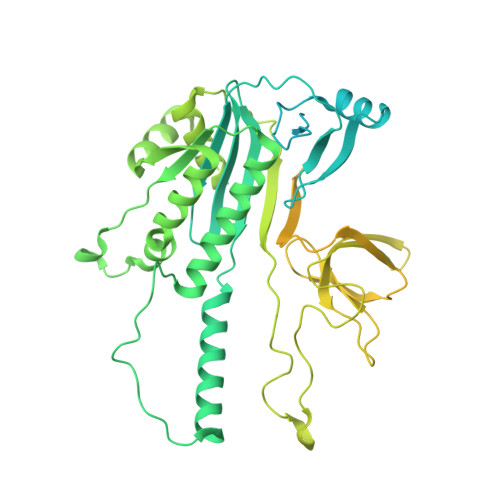
Structure of the OMEGA nickase IsrB in complex with omega RNA and target DNA.
Hirano, S., Kappel, K., Altae-Tran, H., Faure, G., Wilkinson, M.E., Kannan, S., Demircioglu, F.E., Yan, R., Shiozaki, M., Yu, Z., Makarova, K.S., Koonin, E.V., Macrae, R.K., Zhang, F.(2022) Nature 610: 575-581
- PubMed: 36224386
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-022-05324-6
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8DMB - PubMed Abstract:
RNA-guided systems, such as CRISPR-Cas, combine programmable substrate recognition with enzymatic function, a combination that has been used advantageously to develop powerful molecular technologies 1,2 . Structural studies of these systems have illuminated how the RNA and protein jointly recognize and cleave their substrates, guiding rational engineering for further technology development 3 . Recent work identified a new class of RNA-guided systems, termed OMEGA, which include IscB, the likely ancestor of Cas9, and the nickase IsrB, a homologue of IscB lacking the HNH nuclease domain 4 . IsrB consists of only around 350 amino acids, but its small size is counterbalanced by a relatively large RNA guide (roughly 300-nt ωRNA). Here, we report the cryogenic-electron microscopy structure of Desulfovirgula thermocuniculi IsrB (DtIsrB) in complex with its cognate ωRNA and a target DNA. We find the overall structure of the IsrB protein shares a common scaffold with Cas9. In contrast to Cas9, however, which uses a recognition (REC) lobe to facilitate target selection, IsrB relies on its ωRNA, part of which forms an intricate ternary structure positioned analogously to REC. Structural analyses of IsrB and its ωRNA as well as comparisons to other RNA-guided systems highlight the functional interplay between protein and RNA, advancing our understanding of the biology and evolution of these diverse systems.
- Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard, Cambridge, MA, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: