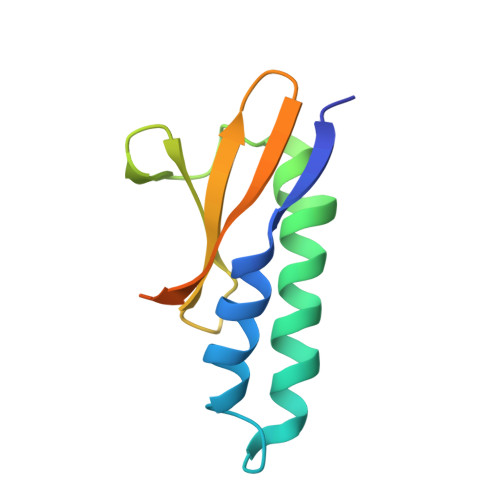
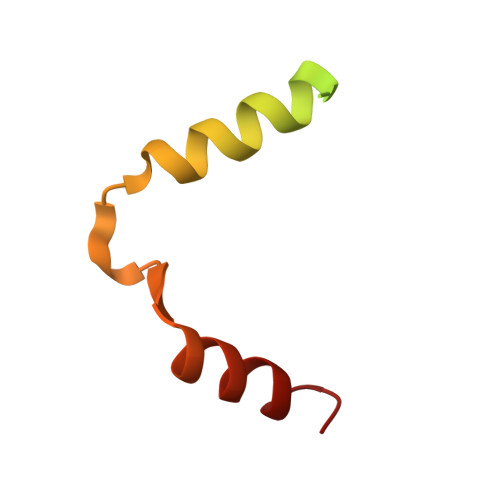
Toxin release by conditional remodelling of ParDE1 from Mycobacterium tuberculosis leads to gyrase inhibition.
Beck, I.N., Arrowsmith, T.J., Grobbelaar, M.J., Bromley, E.H.C., Marles-Wright, J., Blower, T.R.(2024) Nucleic Acids Res 52: 1909-1929
- PubMed: 38113275
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkad1220
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8C24, 8C26 - PubMed Abstract:
Mycobacterium tuberculosis, the causative agent of tuberculosis, is a growing threat to global health, with recent efforts towards its eradication being reversed in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic. Increasing resistance to gyrase-targeting second-line fluoroquinolone antibiotics indicates the necessity to develop both novel therapeutics and our understanding of M. tuberculosis growth during infection. ParDE toxin-antitoxin systems also target gyrase and are regulated in response to both host-associated and drug-induced stress during infection. Here, we present microbiological, biochemical, structural, and biophysical analyses exploring the ParDE1 and ParDE2 systems of M. tuberculosis H37Rv. The structures reveal conserved modes of toxin-antitoxin recognition, with complex-specific interactions. ParDE1 forms a novel heterohexameric ParDE complex, supported by antitoxin chains taking on two distinct folds. Curiously, ParDE1 exists in solution as a dynamic equilibrium between heterotetrameric and heterohexameric complexes. Conditional remodelling into higher order complexes can be thermally driven in vitro. Remodelling induces toxin release, tracked through concomitant inhibition and poisoning of gyrase activity. Our work aids our understanding of gyrase inhibition, allowing wider exploration of toxin-antitoxin systems as inspiration for potential therapeutic agents.
- Department of Biosciences, Durham University, South Road, Durham DH1 3LE, UK.
Organizational Affiliation: