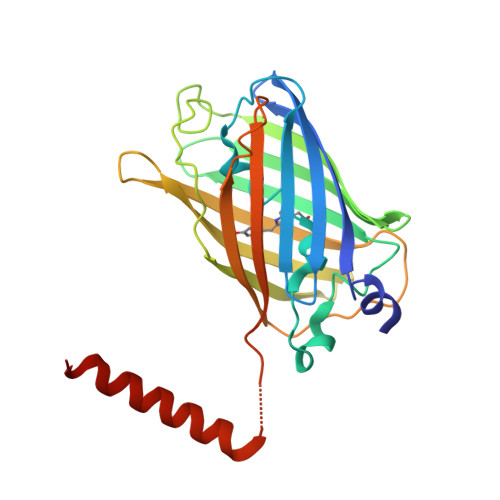
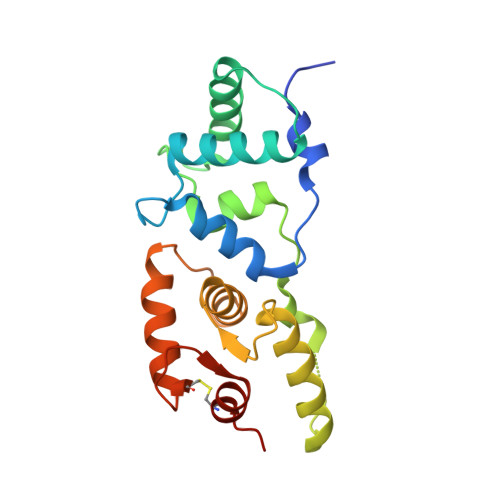
A hydrophobic groove in secretagogin allows for alternate interactions with SNAP-25 and syntaxin-4 in endocrine tissues.
Szodorai, E., Hevesi, Z., Wagner, L., Hokfelt, T.G.M., Harkany, T., Schnell, R.(2024) Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 121: e2309211121-e2309211121
- PubMed: 38593081
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2309211121
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
8BAN, 8BAV, 8BBJ - PubMed Abstract:
Vesicular release of neurotransmitters and hormones relies on the dynamic assembly of the exocytosis/trans-SNARE complex through sequential interactions of synaptobrevins, syntaxins, and SNAP-25. Despite SNARE-mediated release being fundamental for intercellular communication in all excitable tissues, the role of auxiliary proteins modulating the import of reserve vesicles to the active zone, and thus, scaling repetitive exocytosis remains less explored. Secretagogin is a Ca 2+ -sensor protein with SNAP-25 being its only known interacting partner. SNAP-25 anchors readily releasable vesicles within the active zone, thus being instrumental for 1st phase release. However, genetic deletion of secretagogin impedes 2nd phase release instead, calling for the existence of alternative protein-protein interactions. Here, we screened the secretagogin interactome in the brain and pancreas, and found syntaxin-4 grossly overrepresented. Ca 2+ -loaded secretagogin interacted with syntaxin-4 at nanomolar affinity and 1:1 stoichiometry. Crystal structures of the protein complexes revealed a hydrophobic groove in secretagogin for the binding of syntaxin-4. This groove was also used to bind SNAP-25. In mixtures of equimolar recombinant proteins, SNAP-25 was sequestered by secretagogin in competition with syntaxin-4. K d differences suggested that secretagogin could shape unidirectional vesicle movement by sequential interactions, a hypothesis supported by in vitro biological data. This mechanism could facilitate the movement of transport vesicles toward release sites, particularly in the endocrine pancreas where secretagogin, SNAP-25, and syntaxin-4 coexist in both α- and β-cells. Thus, secretagogin could modulate the pace and fidelity of vesicular hormone release by differential protein interactions.
- Division of Molecular and Cellular Neuroendocrinology, Department of Neuroscience, Biomedicum 7D, Karolinska Institutet, Solna SE-17165, Sweden.
Organizational Affiliation: