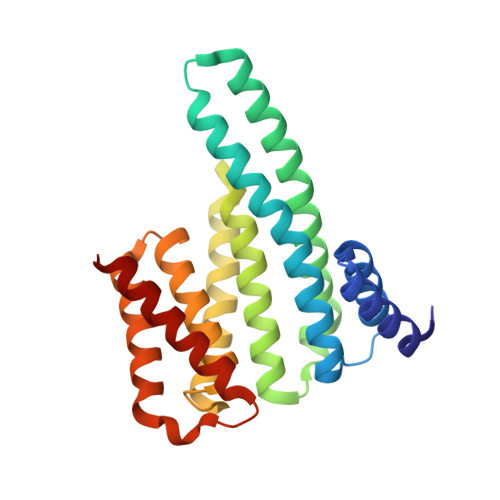
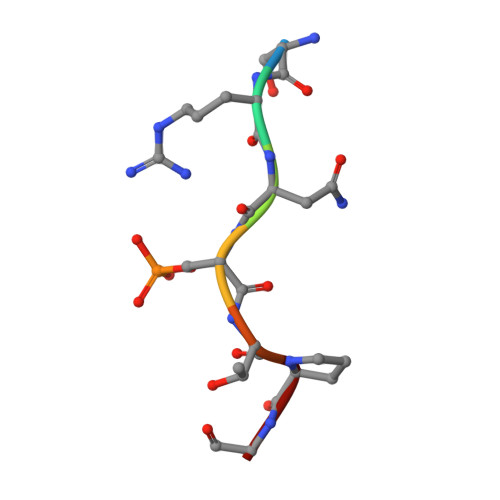
Structural basis for SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid (N) protein recognition by 14-3-3 proteins.
Eisenreichova, A., Boura, E.(2022) J Struct Biol 214: 107879-107879
- PubMed: 35781025
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsb.2022.107879
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7ZIT - PubMed Abstract:
14-3-3 proteins are important dimeric scaffolds that regulate the function of hundreds of proteins in a phosphorylation-dependent manner. The SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid (N) protein forms a complex with human 14-3-3 proteins upon phosphorylation, which has also been described for other coronaviruses. Here, we report a high-resolution crystal structure of 14-3-3 bound to an N phosphopeptide bearing the phosphoserine 197 in the middle. The structure revealed two copies of the N phosphopeptide bound, each in the central binding groove of each 14-3-3 monomer. A complex network of hydrogen bonds and water bridges between the peptide and 14-3-3 was observed explaining the high affinity of the N protein for 14-3-3 proteins.
- Institute of Organic Chemistry and Biochemistry AS CR, v.v.i., Flemingovo nam. 2, 166 10 Prague 6, Czech Republic.
Organizational Affiliation: