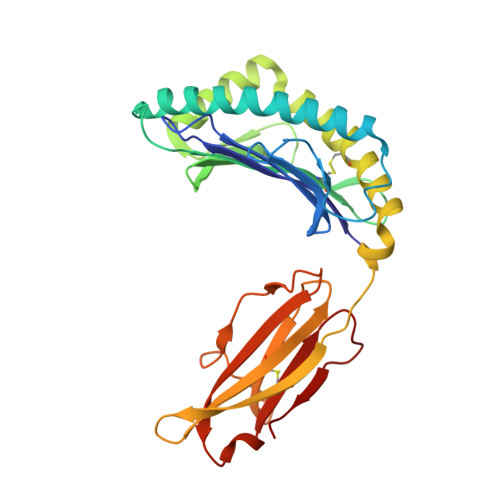
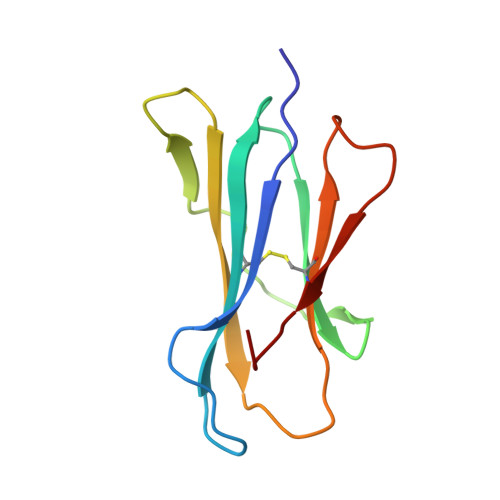
Structural Analyses of a Dominant Cryptosporidium parvum Epitope Presented by H-2K b Offer New Options To Combat Cryptosporidiosis.
Wang, Y., Gao, M., Li, X., Zhu, W., Zhao, M., Li, J., Liu, X., Cao, L., Li, S., Zhang, S., Zhang, L., Fan, S.(2023) mBio 14: e0266622-e0266622
- PubMed: 36602309
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1128/mbio.02666-22
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7WCY - PubMed Abstract:
Cryptosporidium parvum has gained much attention as a major cause of diarrhea in the world, particularly in those with compromised immune systems. The data currently available on how the immune system recognizes C. parvum are growing rapidly, but we lack data on the interactions among host major histocompatibility complex (MHC) diversity and parasitic T-cell epitopes. To identify antigenic epitopes in a murine model, we performed systematic profiling of H-2K b -restricted peptides by screening the dominant Cryptosporidium antigens. The results revealed that the glycoprotein-derived epitope Gp40/15-SVF9 induced an immunodominant response in C. parvum-recovered C57BL/6 mice, and injection of the cytotoxic-T-lymphocyte (CTL) peptide with the adjuvant activated peptide-specific CD8 + T cells. Notably, the SVF9 epitope was highly conserved across Cryptosporidium hominis, C. parvum, and many other Cryptosporidium species. SVF9 also formed stable peptide-MHC class I (MHC I) complexes with HLA-A*0201, suggesting cross-reactivity between H-2K b and human MHC I specificities. Crystal structure analyses revealed that the interactions of peptide-MHC surface residues of H-2K b and HLA-A*0201 are highly conserved. The hydrogen bonds of H-2K b -SVF9 are similar to those of a dominant epitope presented by HLA-A*0201, which can be recognized by a public human T-cell receptor (TCR). Notably, we found double conformations in position 4 (P4), 5 (P5) of the SVF9 peptide, which showed high flexibility, and multiple peptide conformations generated more molecular surfaces that can potentially be recognized by TCRs. Our findings demonstrate that an immunodominant C. parvum epitope and its homologs from different Cryptosporidium species and subtypes can benefit vaccine development to combat cryptosporidiosis. IMPORTANCE Adaptive immune responses and T lymphocytes have been implicated as important mechanisms of parasite-induced protection. However, the role of CD8 + T lymphocytes in the resolution of C. parvum infection is largely unresolved. Our results revealed that the glycoprotein-derived epitope Gp40/15-SVF9 induced an immunodominant CD8 + T-cell response in C57BL/6 mice. Crystal structure analyses revealed that the interactions of the H-2K b -SVF9 peptide are similar to those of a dominant epitope presented by HLA-A*0201, which can be recognized by human TCRs. In addition, we found double conformations of the SVF9 peptide, which showed high flexibility and multiple peptide conformations that can potentially be recognized by TCRs.
- College of Life Science and Agronomy, Zhoukou Normal University, Zhoukou, People's Republic of China.
Organizational Affiliation: