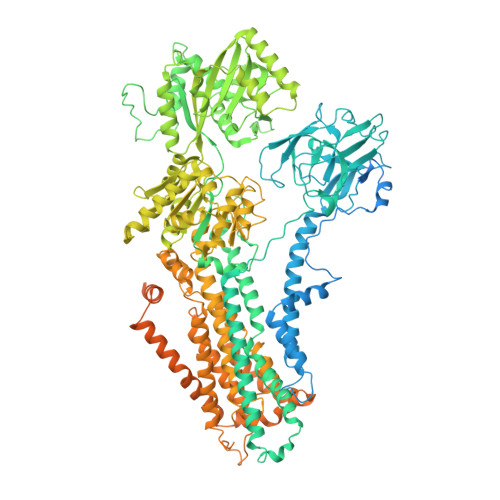
Structural basis of substrate-independent phosphorylation in a P4-ATPase lipid flippase
Timcenko, M., Dieudonne, T., Montigny, C., Boesen, T., Lyons, J.A., Lenoir, G., Nissen, P.(2021) J Mol Biology : 167062
- PubMed: 34023399
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2021.167062
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7OH4, 7OH5, 7OH6, 7OH7 - PubMed Abstract:
P4-ATPases define a eukaryotic subfamily of the P-type ATPases, and are responsible for the transverse flip of specific lipids from the extracellular or luminal leaflet to the cytosolic leaflet of cell membranes. The enzymatic cycle of P-type ATPases is divided into autophosphorylation and dephosphorylation half-reactions. Unlike most other P-type ATPases, P4-ATPases transport their substrate during dephosphorylation only, i.e. the phosphorylation half-reaction is not associated with transport. To study the structural basis of the distinct mechanisms of P4-ATPases, we have determined cryo-EM structures of Drs2p-Cdc50p from Saccharomyces cerevisiae covering multiple intermediates of the cycle. We identify several structural motifs specific to Drs2p and P4-ATPases in general that decrease movements and flexibility of domains as compared to other P-type ATPases such as Na + /K + -ATPase or Ca 2+ -ATPase. These motifs include the linkers that connect the transmembrane region to the actuator (A) domain, which is responsible for dephosphorylation. Additionally, mutation of Tyr380, which interacts with conserved Asp340 of the distinct DGET dephosphorylation loop of P4-ATPases, highlights a functional role of these P4-ATPase specific motifs in the A-domain. Finally, the transmembrane (TM) domain, responsible for transport, also undergoes less extensive conformational changes, which is ensured both by a longer segment connecting TM helix 4 with the phosphorylation site, and possible stabilization by the auxiliary subunit Cdc50p. Collectively these adaptions in P4-ATPases are responsible for phosphorylation becoming transport-independent.
- Danish Research Institute of Translational Neuroscience - DANDRITE, Nordic EMBL Partnerhip for Molecular Medicine, Aarhus University, Dept. Molecular Biology and Genetics, Gustav Wieds Vej 10C, DK - 8000 Aarhus C, Denmark.
Organizational Affiliation: