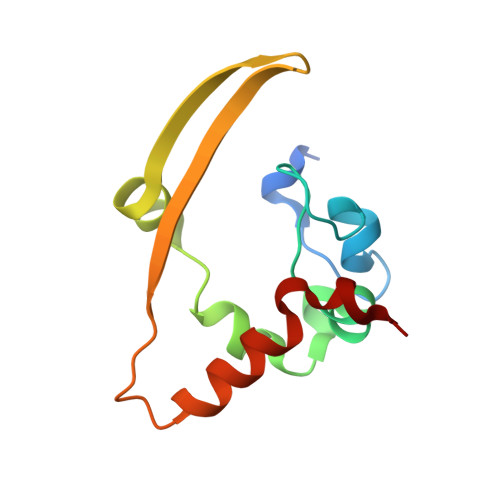
Structural Insight Into the SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid Protein C-Terminal Domain Reveals a Novel Recognition Mechanism for Viral Transcriptional Regulatory Sequences.
Yang, M., He, S., Chen, X., Huang, Z., Zhou, Z., Zhou, Z., Chen, Q., Chen, S., Kang, S.(2020) Front Chem 8: 624765-624765
- PubMed: 33511102
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3389/fchem.2020.624765
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7DE1 - PubMed Abstract:
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) has caused massive disruptions to society and the economy, and the transcriptional regulatory mechanisms behind the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) are poorly understood. Herein, we determined the crystal structure of the SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein C-terminal domain (CTD) at a resolution of 2.0 Å, and demonstrated that the CTD has a comparable distinct electrostatic potential surface to equivalent domains of other reported CoVs, suggesting that the CTD has novel roles in viral RNA binding and transcriptional regulation. Further in vitro biochemical assays demonstrated that the viral genomic intergenic transcriptional regulatory sequences (TRSs) interact with the SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid protein CTD with a flanking region. The unpaired adeno dinucleotide in the TRS stem-loop structure is a major determining factor for their interactions. Taken together, these results suggested that the nucleocapsid protein CTD is responsible for the discontinuous viral transcription mechanism by recognizing the different patterns of viral TRS during transcription.
- Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Biomedical Imaging, Molecular Imaging Center, The Fifth Affiliated Hospital, Sun Yat-sen University, Zhuhai, China.
Organizational Affiliation: