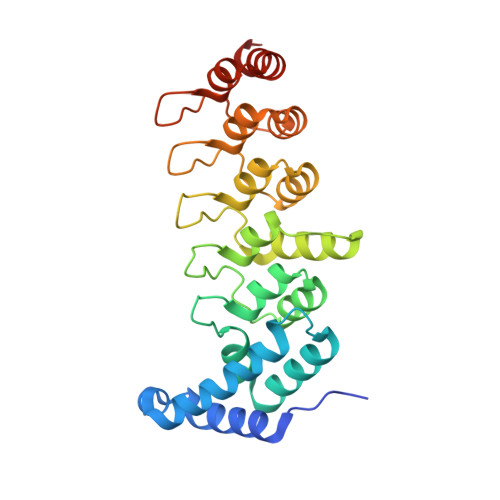
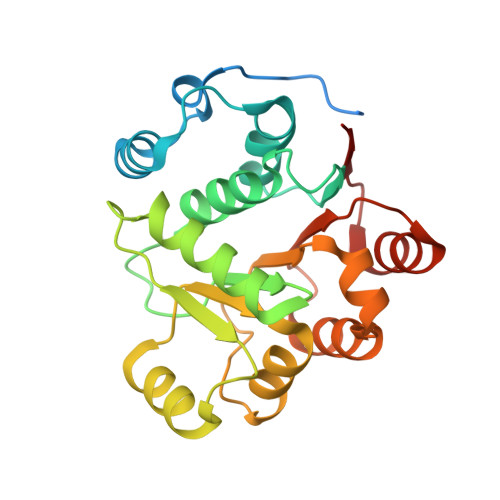
Nephrotic-syndrome-associated mutation of KANK2 induces pathologic binding competition with physiological interactor KIF21A.
Xu, Y., Guo, C., Pan, W., Zhao, C., Ding, Y., Xie, X., Wei, Z., Sun, Y., Yu, C.(2021) J Biological Chem 297: 100958-100958
- PubMed: 34274317
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbc.2021.100958
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7DDX - PubMed Abstract:
Nephrotic syndrome (NS) is a common kidney disorder caused by dysfunction of the glomerular filtration barrier. Some genetic mutations identified in NS patients cause amino acid substitutions of kidney ankyrin repeat-containing (KANK) proteins, which are scaffold proteins that regulate actin polymerization, microtubule targeting, and cell adhesion via binding to various molecules, including the kinesin motor protein KIF21A. However, the mechanisms by which these mutations lead to NS are unclear. Here, we unexpectedly found that the eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4A1 (eIF4A1) interacts with an NS-associated KANK2 mutant (S684F) but not the wild-type protein. Biochemical and structural analyses revealed that the pathological mutation induces abnormal binding of eIF4A1 to KANK2 at the physiological KIF21A-binding site. Competitive binding assays further indicated that eIF4A1 can compete with KIF21A to interact with the S684F mutant of KANK2. In cultured mouse podocytes, this S684F mutant interfered with the KANK2/KIF21A interaction by binding to eIF4A1, and failed to rescue the focal adhesion or cell adhesion that had been reduced or morphologically changed by KANK2 knockout. These structural, biochemical, and cellular results not only provide mechanistic explanations for the podocyte defects caused by the S684F mutation, but also show how a gain-of-binding mutation can lead to a loss-of-function effect.
- Department of Biology, School of Life Sciences, Southern University of Science and Technology, Shenzhen, Guangdong, China.
Organizational Affiliation: