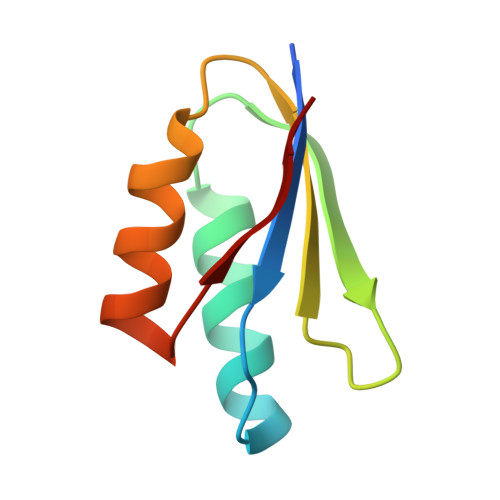
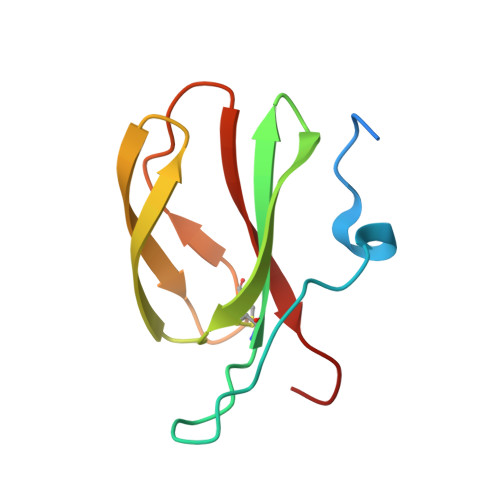
Two NLR immune receptors acquired high-affinity binding to a fungal effector through convergent evolution of their integrated domain.
Bialas, A., Langner, T., Harant, A., Contreras, M.P., Stevenson, C.E., Lawson, D.M., Sklenar, J., Kellner, R., Moscou, M.J., Terauchi, R., Banfield, M.J., Kamoun, S.(2021) Elife 10
- PubMed: 34288868
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.66961
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
7BNT - PubMed Abstract:
A subset of plant NLR immune receptors carry unconventional integrated domains in addition to their canonical domain architecture. One example is rice Pik-1 that comprises an integrated heavy metal-associated (HMA) domain. Here, we reconstructed the evolutionary history of Pik-1 and its NLR partner, Pik-2, and tested hypotheses about adaptive evolution of the HMA domain. Phylogenetic analyses revealed that the HMA domain integrated into Pik-1 before Oryzinae speciation over 15 million years ago and has been under diversifying selection. Ancestral sequence reconstruction coupled with functional studies showed that two Pik-1 allelic variants independently evolved from a weakly binding ancestral state to high-affinity binding of the blast fungus effector AVR-PikD. We conclude that for most of its evolutionary history the Pik-1 HMA domain did not sense AVR-PikD, and that different Pik-1 receptors have recently evolved through distinct biochemical paths to produce similar phenotypic outcomes. These findings highlight the dynamic nature of the evolutionary mechanisms underpinning NLR adaptation to plant pathogens.
- The Sainsbury Laboratory, University of East Anglia, Norwich Research Park, Norwich, United Kingdom.
Organizational Affiliation: