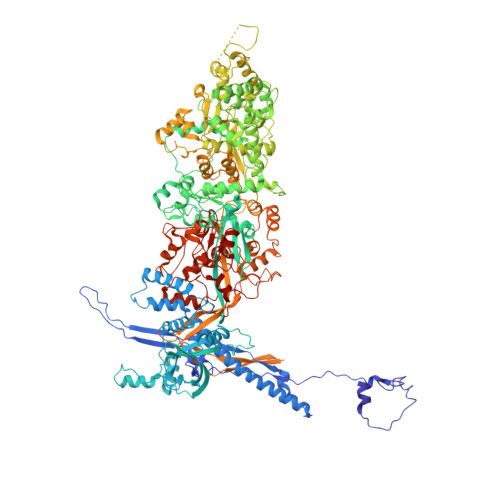
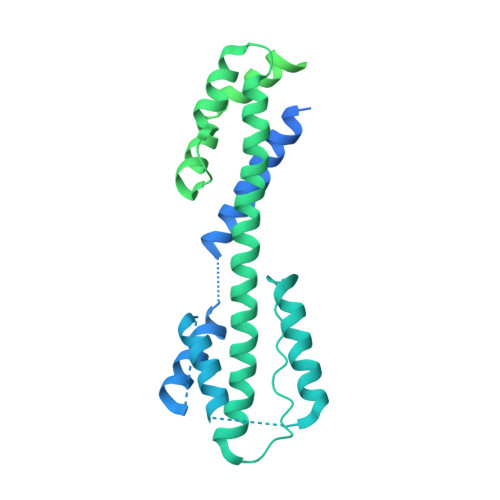
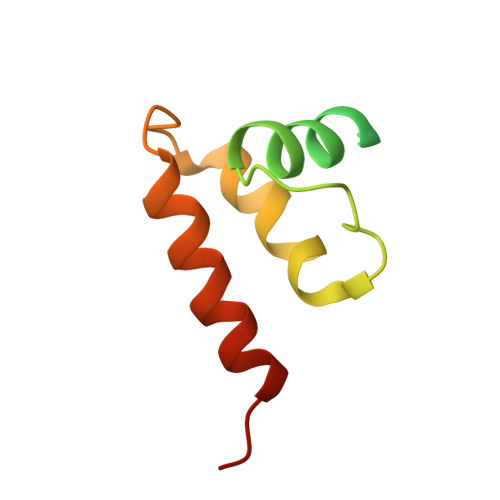
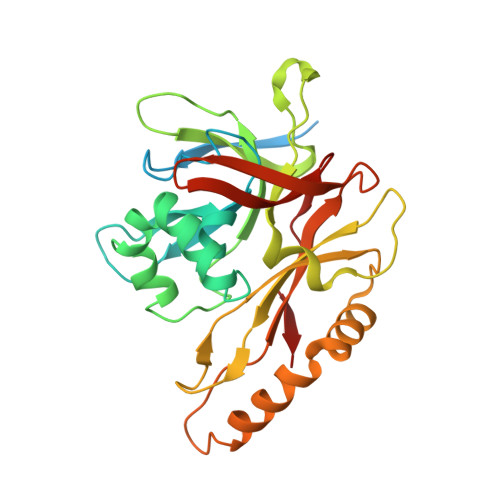
Atomic structures and deletion mutant reveal different capsid-binding patterns and functional significance of tegument protein pp150 in murine and human cytomegaloviruses with implications for therapeutic development.
Liu, W., Dai, X., Jih, J., Chan, K., Trang, P., Yu, X., Balogun, R., Mei, Y., Liu, F., Zhou, Z.H.(2019) PLoS Pathog 15: e1007615-e1007615
- PubMed: 30779794
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1007615
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6NHJ - PubMed Abstract:
Cytomegalovirus (CMV) infection causes birth defects and life-threatening complications in immunosuppressed patients. Lack of vaccine and need for more effective drugs have driven widespread ongoing therapeutic development efforts against human CMV (HCMV), mostly using murine CMV (MCMV) as the model system for preclinical animal tests. The recent publication (Yu et al., 2017, DOI: 10.1126/science.aam6892) of an atomic model for HCMV capsid with associated tegument protein pp150 has infused impetus for rational design of novel vaccines and drugs, but the absence of high-resolution structural data on MCMV remains a significant knowledge gap in such development efforts. Here, by cryoEM with sub-particle reconstruction method, we have obtained the first atomic structure of MCMV capsid with associated pp150. Surprisingly, the capsid-binding patterns of pp150 differ between HCMV and MCMV despite their highly similar capsid structures. In MCMV, pp150 is absent on triplex Tc and exists as a "Λ"-shaped dimer on other triplexes, leading to only 260 groups of two pp150 subunits per capsid in contrast to 320 groups of three pp150 subunits each in a "Δ"-shaped fortifying configuration. Many more amino acids contribute to pp150-pp150 interactions in MCMV than in HCMV, making MCMV pp150 dimer inflexible thus incompatible to instigate triplex Tc-binding as observed in HCMV. While pp150 is essential in HCMV, our pp150-deletion mutant of MCMV remained viable though with attenuated infectivity and exhibiting defects in retaining viral genome. These results thus invalidate targeting pp150, but lend support to targeting capsid proteins, when using MCMV as a model for HCMV pathogenesis and therapeutic studies.
- State Key Laboratory of Precision Spectroscopy, School of Physics and Material Science, East China Normal University, Shanghai, China.
Organizational Affiliation: