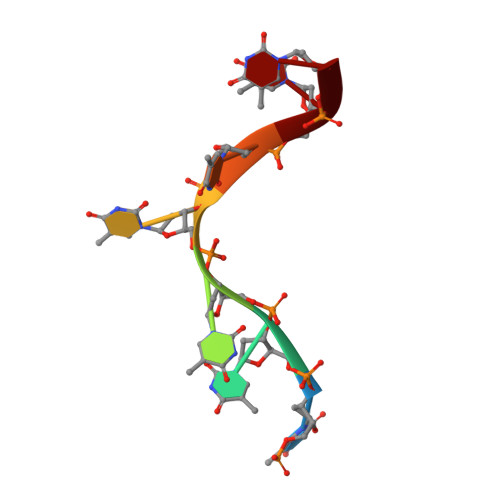
Structural insights into nanoRNA degradation by human Rexo2.
Chu, L.Y., Agrawal, S., Chen, Y.P., Yang, W.Z., Yuan, H.S.(2019) RNA 25: 737-746
- PubMed: 30926754
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1261/rna.070557.119
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6J7Y, 6J7Z, 6J80 - PubMed Abstract:
Human RNA exoribonuclease 2 (Rexo2) is an evolutionarily conserved 3'-to-5' DEDDh-family exonuclease located primarily in mitochondria. Rexo2 degrades small RNA oligonucleotides of <5 nucleotides (nanoRNA) in a way similar to Escherichia coli Oligoribonuclease (ORN), suggesting that it plays a role in RNA turnover in mitochondria. However, how Rexo2 preferentially binds and degrades nanoRNA remains elusive. Here, we show that Rexo2 binds small RNA and DNA oligonucleotides with the highest affinity, and it is most robust in degrading small nanoRNA into mononucleotides in the presence of magnesium ions. We further determined three crystal structures of Rexo2 in complex with single-stranded RNA or DNA at resolutions of 1.8-2.2 Å. Rexo2 forms a homodimer and interacts mainly with the last two 3'-end nucleobases of substrates by hydrophobic and π-π stacking interactions via Leu53, Trp96, and Tyr164, signifying its preference in binding and degrading short oligonucleotides without sequence specificity. Crystal structure of Rexo2 is highly similar to that of the RNA-degrading enzyme ORN, revealing a two-magnesium-ion-dependent hydrolysis mechanism. This study thus provides the molecular basis for human Rexo2, showing how it binds and degrades nanoRNA into nucleoside monophosphates and plays a crucial role in RNA salvage pathways in mammalian mitochondria.
- Institute of Molecular Biology, Academia Sinica, Taipei, Taiwan 11529, Republic of China.
Organizational Affiliation: