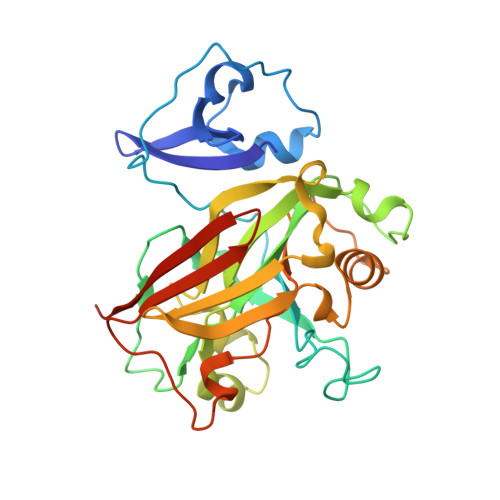
Structural and functional analysis of a dimeric fumarylacetoacetate hydrolase (EaFAH) from psychrophilic Exiguobacterium antarcticum.
Yoo, W., Lee, C.W., Kim, B.Y., Huong Luu Le, L.T., Park, S.H., Kim, H.W., Shin, S.C., Kim, K.K., Lee, J.H., Kim, T.D.(2019) Biochem Biophys Res Commun 509: 773-778
- PubMed: 30630595
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.12.183
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6IYM - PubMed Abstract:
Fumarylacetoacetate hydrolase (FAH) is essential for the degradation of aromatic amino acids as well as for the cleavage of carbon-carbon bonds in metabolites or small organic compounds. Here, the X-ray crystal structure of EaFAH, a dimeric fumarylacetoacetate hydrolase from Exiguobacterium antarcticum, was determined, and its functional properties were investigated using biochemical methods. EaFAH adopts a mixed β-sandwich roll fold with a highly flexible lid region (Val 73 -Leu 94 ), and an Mg 2+ ion is bound at the active site by coordinating to the three carboxylate oxygen atoms of Glu 124 , Glu 126 , and Asp 155 . The hydrolytic activity of EaFAH toward various substrates, including linalyl acetate was investigated using native polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, activity staining, gel filtration, circular dichroism spectroscopy, fluorescence, and enzyme assays.
- Department of Chemistry, College of Natural Science, Sookmyung Women's University, Seoul, 04310, South Korea; Department of Molecular Cell Biology, Samsung Biomedical Research Institute, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Suwon, 440-746, South Korea.
Organizational Affiliation: