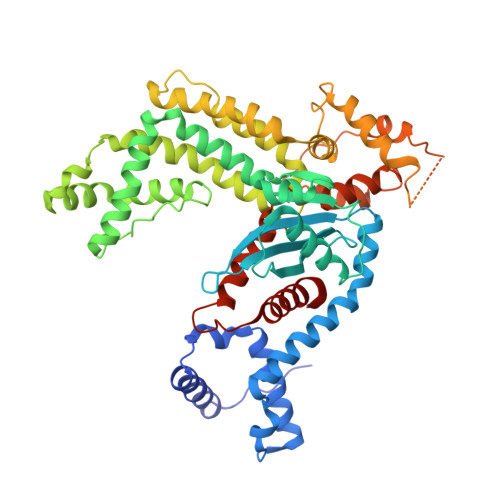
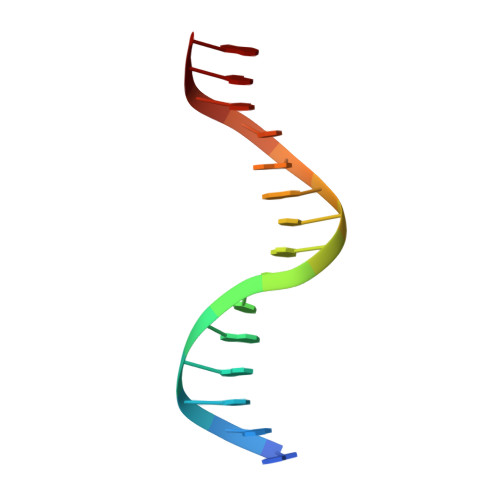
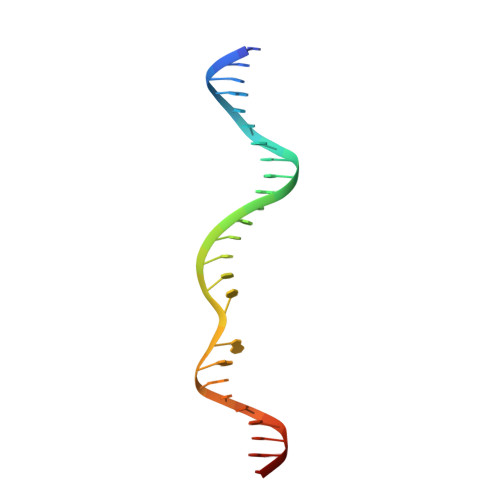
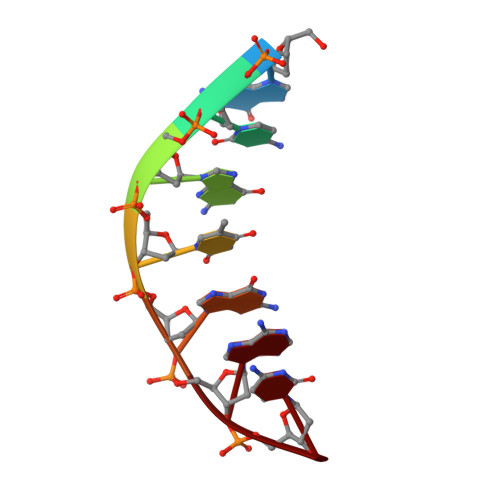
Structural insights into the mechanism of double strand break formation by Hermes, a hAT family eukaryotic DNA transposase.
Hickman, A.B., Voth, A.R., Ewis, H., Li, X., Craig, N.L., Dyda, F.(2018) Nucleic Acids Res 46: 10286-10301
- PubMed: 30239795
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gky838
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6DWW, 6DWY, 6DWZ, 6DX0 - PubMed Abstract:
Some DNA transposons relocate from one genomic location to another using a mechanism that involves generating double-strand breaks at their transposon ends by forming hairpins on flanking DNA. The same double-strand break mode is employed by the V(D)J recombinase at signal-end/coding-end junctions during the generation of antibody diversity. How flanking hairpins are formed during DNA transposition has remained elusive. Here, we describe several co-crystal structures of the Hermes transposase bound to DNA that mimics the reaction step immediately prior to hairpin formation. Our results reveal a large DNA conformational change between the initial cleavage step and subsequent hairpin formation that changes which strand is acted upon by a single active site. We observed that two factors affect the conformational change: the complement of divalent metal ions bound by the catalytically essential DDE residues, and the identity of the -2 flanking base pair. Our data also provides a mechanistic link between the efficiency of hairpin formation (an A:T basepair is favored at the -2 position) and Hermes' strong target site preference. Furthermore, we have established that the histidine residue within a conserved C/DxxH motif present in many transposase families interacts directly with the scissile phosphate, suggesting a crucial role in catalysis.
- Laboratory of Molecular Biology, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD 20892, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: