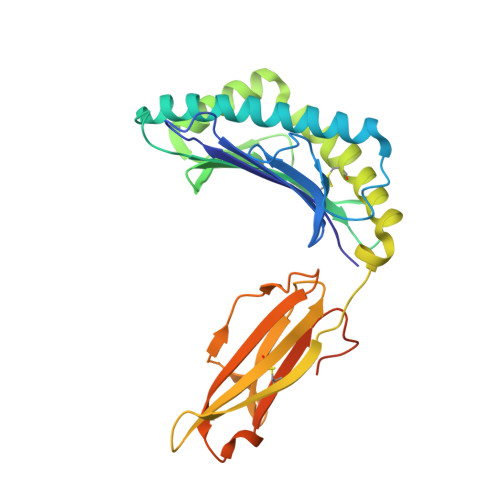
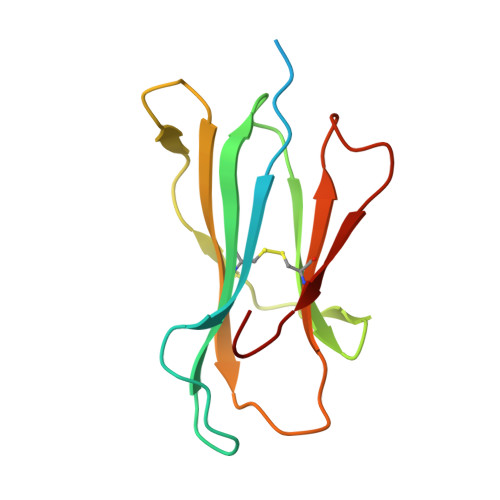
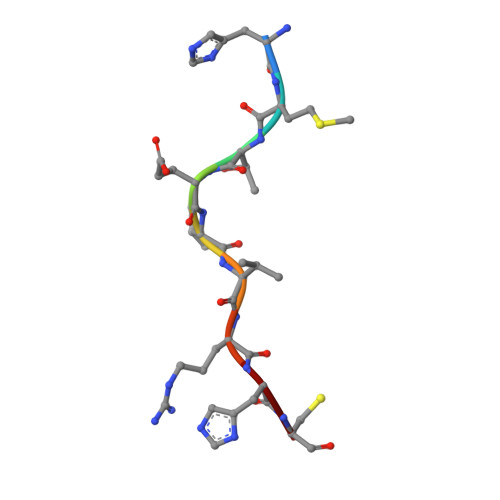
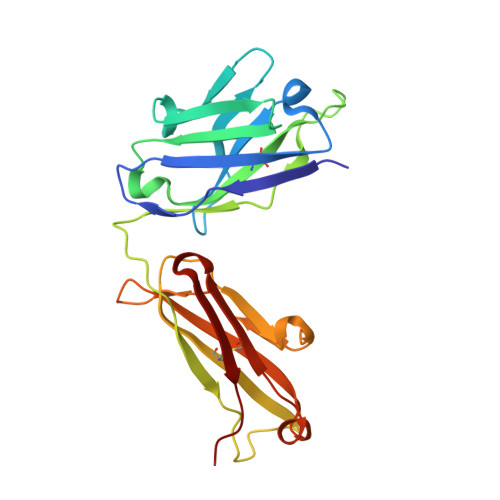
Targeting a neoantigen derived from a common TP53 mutation.
Hsiue, E.H., Wright, K.M., Douglass, J., Hwang, M.S., Mog, B.J., Pearlman, A.H., Paul, S., DiNapoli, S.R., Konig, M.F., Wang, Q., Schaefer, A., Miller, M.S., Skora, A.D., Azurmendi, P.A., Murphy, M.B., Liu, Q., Watson, E., Li, Y., Pardoll, D.M., Bettegowda, C., Papadopoulos, N., Kinzler, K.W., Vogelstein, B., Gabelli, S.B., Zhou, S.(2021) Science 371
- PubMed: 33649166
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.1126/science.abc8697
- Primary Citation of Related Structures:
6W51 - PubMed Abstract:
TP53 (tumor protein p53) is the most commonly mutated cancer driver gene, but drugs that target mutant tumor suppressor genes, such as TP53 , are not yet available. Here, we describe the identification of an antibody highly specific to the most common TP53 mutation (R175H, in which arginine at position 175 is replaced with histidine) in complex with a common human leukocyte antigen-A (HLA-A) allele on the cell surface. We describe the structural basis of this specificity and its conversion into an immunotherapeutic agent: a bispecific single-chain diabody. Despite the extremely low p53 peptide-HLA complex density on the cancer cell surface, the bispecific antibody effectively activated T cells to lyse cancer cells that presented the neoantigen in vitro and in mice. This approach could in theory be used to target cancers containing mutations that are difficult to target in conventional ways.
- Ludwig Center, Sidney Kimmel Comprehensive Cancer Center, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD 21287, USA.
Organizational Affiliation: